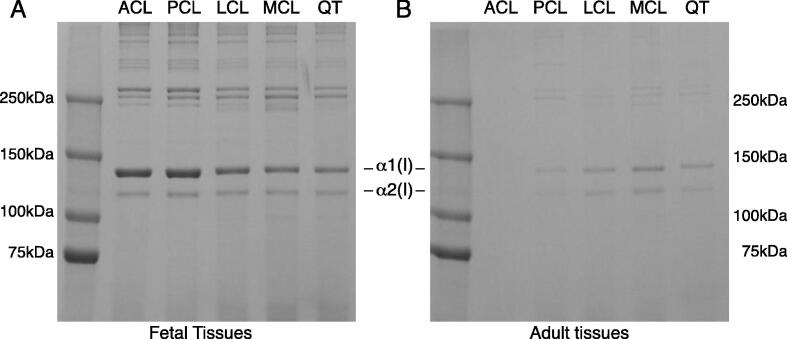
Fig. 1.
SDS-PAGE reveals a decrease in collagen extractability in adult tendons and ligaments compared to fetal tissue. Acid labile aldimine cross-links are broken with mild acetic acid treatment, allowing native type I collagen monomers to be extracted from the tissue. Collagen was more acid extractable from fetal tissues (A) than adult tissues (B). Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), lateral collateral ligament (LCL), medial collateral ligament (MCL), quadriceps tendon (QT). SDS-PAGE sample loads were normalized to the dry weight of lyophilized tissues. The reduction in collagen extractability from adult tissues is consistent with an increase in mature collagen cross-links with development.