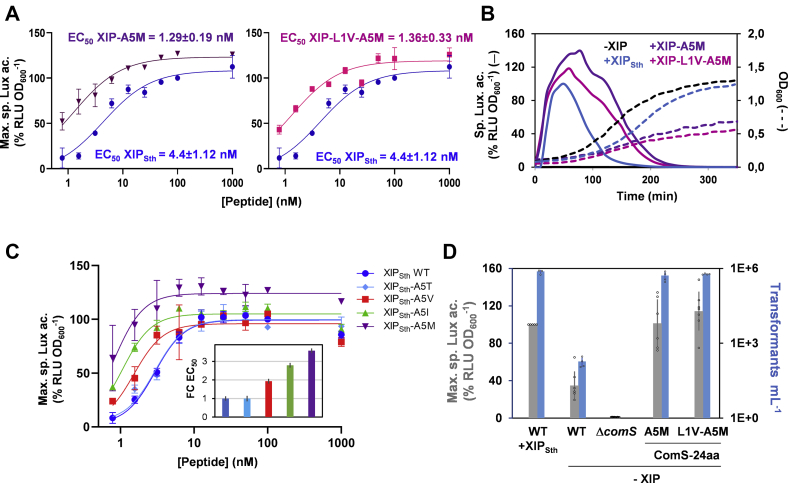
Figure 2.
In vivo effect of synthetic pheromone variants.A, dose response of PcomS activity upon addition of synthetic (8 aa) XIPSth WT (blue), XIP-A5M (purple), or XIP-L1V-A5M (fuchsia). Maximum specific luciferase activity (% RLU × OD600−1) was monitored by using a S. thermophilus ΔcomS reporter strain (PcomS-luxAB). The value obtained in the presence of 100 nM XIPSth was used as reference. Plots were fitted with the Hill equation to calculate the EC50 values that are indicated in the graphs. B, kinetics of luciferase activation (solid lines) and growth curves (dotted lines) of the reporter strain upon addition (100 nM) of synthetic XIPSth WT (blue), XIP-A5M (purple), or XIP-L1V-A5M (fuchsia), or in absence of peptide (black). C, dose response of PcomS activity upon addition of synthetic XIPSth WT (blue), or XIP-5 variants: XIP-A5T (light blue), XIP-A5V (red), XIP-A5I (green), or XIP-A5M (purple). The monitoring of luciferase activity and estimation of EC50 were performed as in panel A. The inset represents the fold change (FC) in EC50 of each XIP-5 variant using as reference the EC50 of XIPSth WT. Increase in fold change is representative of a decrease in EC50 compared with XIPSth WT fixed at 1. D, maximum specific luciferase activity (% RLU × OD600−1; gray bars) and transformation efficiency (transformants × ml−1; blue bars) of S. thermophilus reporter strains producing the full-length precursor ComS-24aa WT, ComS-24aa-A5M or ComS-24aa-L1V-A5M. S. thermophilus WT in the presence of 100 nM XIPSth and a ΔcomS mutant strain were included as positive and negative control, respectively. The WT strain in the presence of XIPSth is used as reference to normalize the maximum specific luciferase activity. In A, C, and D, experimental values represent the mean ± SD of at least three independent replicates.