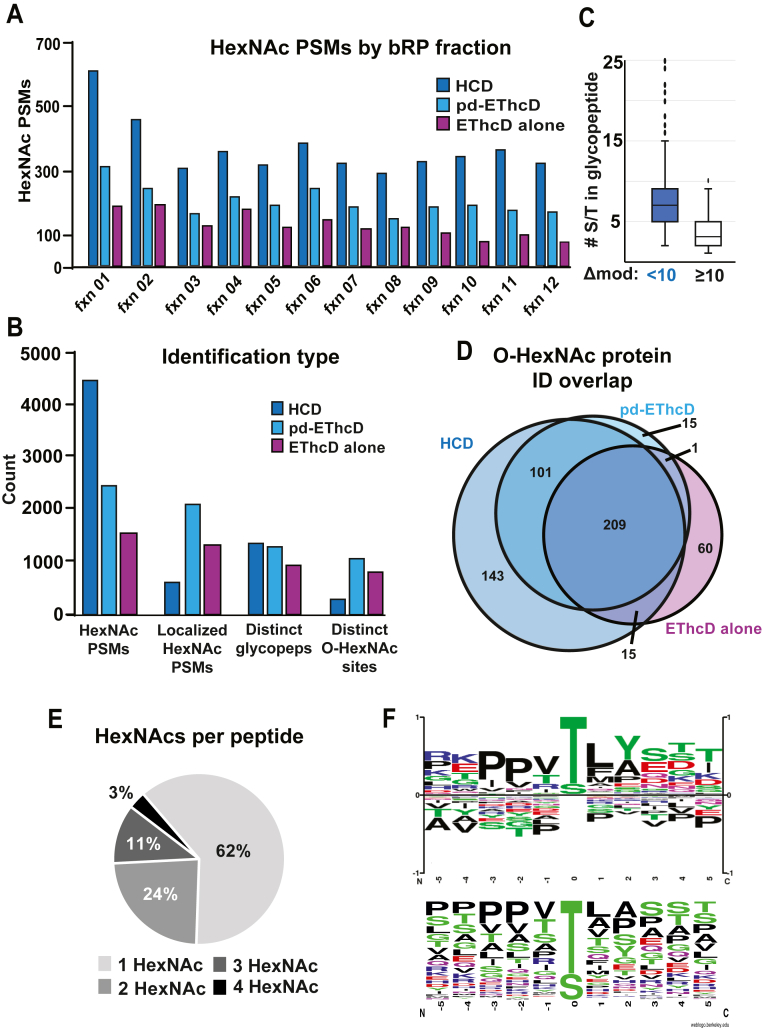
Fig. 4.
Benchmarking anti-O-GlcNAc antibodies with postsynaptic density preparations across different data acquisition methods.A, HexNAc-containing PSMs across basic reversed-phase fractions. Blue bars indicate the number of HexNAc-containing PSMs identified by HCD or the subsequent pd-EThcD scan. Purple bars indicate the number of HexNAc-containing PSMs from EThcD alone. B, breakdown of various identifications from the cumulative analysis analyzing O-GlcNAc peptides from mouse synaptosome fractions. “HexNAc PSMs” refer to PSMs that contain at least one HexNAc modification, regardless of localization. “Localized HexNAc PSMs” refer to all glycosylation sites within HexNAc-containing PSMs that had a Delta Mod Score of 10 or greater. “Distinct Glycopeps” refers to nonredundant glycopeptides identified by the respective dissociation mode. However, HCD-based identifications were treated as if site localization could not be used (see Experimental Procedures). “Distinct O-HexNAc sites” refer to the count of HexNAc site assignments from all sites within nonredundant HexNAc-containing PSMs with Delta Mod Score of 10 or greater. C, number of S/T residues within HCD-based glycopeptide identifications with a Delta Mod Score of less than 10 (blue box) or 10 or greater (white box) to symbolize the trend HCD mostly identifies O-HexNAc sites in peptide with few amino acid possibilities for modification. D, overlap of proteins identified as O-HexNAc modified by the respective data acquisition methods. Only a single HexNAc-containing PSM was required to be called an O-GlcNAc-modified protein. “pd-EThcD” indicates the EThcD scan triggered from the detection of HexNAc fragment ions in the antecedent HCD scan. E, distribution of the extent of HexNAc modifications of HexNAc-containing PSMs across all high-confidence HexNAc-containing PSMs. F, sequence logo of distinct O-HexNAc sites according to two different analysis methods (see Experimental Procedures). The top logo was derived from Phosphosite.org; the bottom from Weblogo (Berkeley).