Figure 4. Robo2 is part of a heterophilic complex with presynaptic Neurexins in trans.
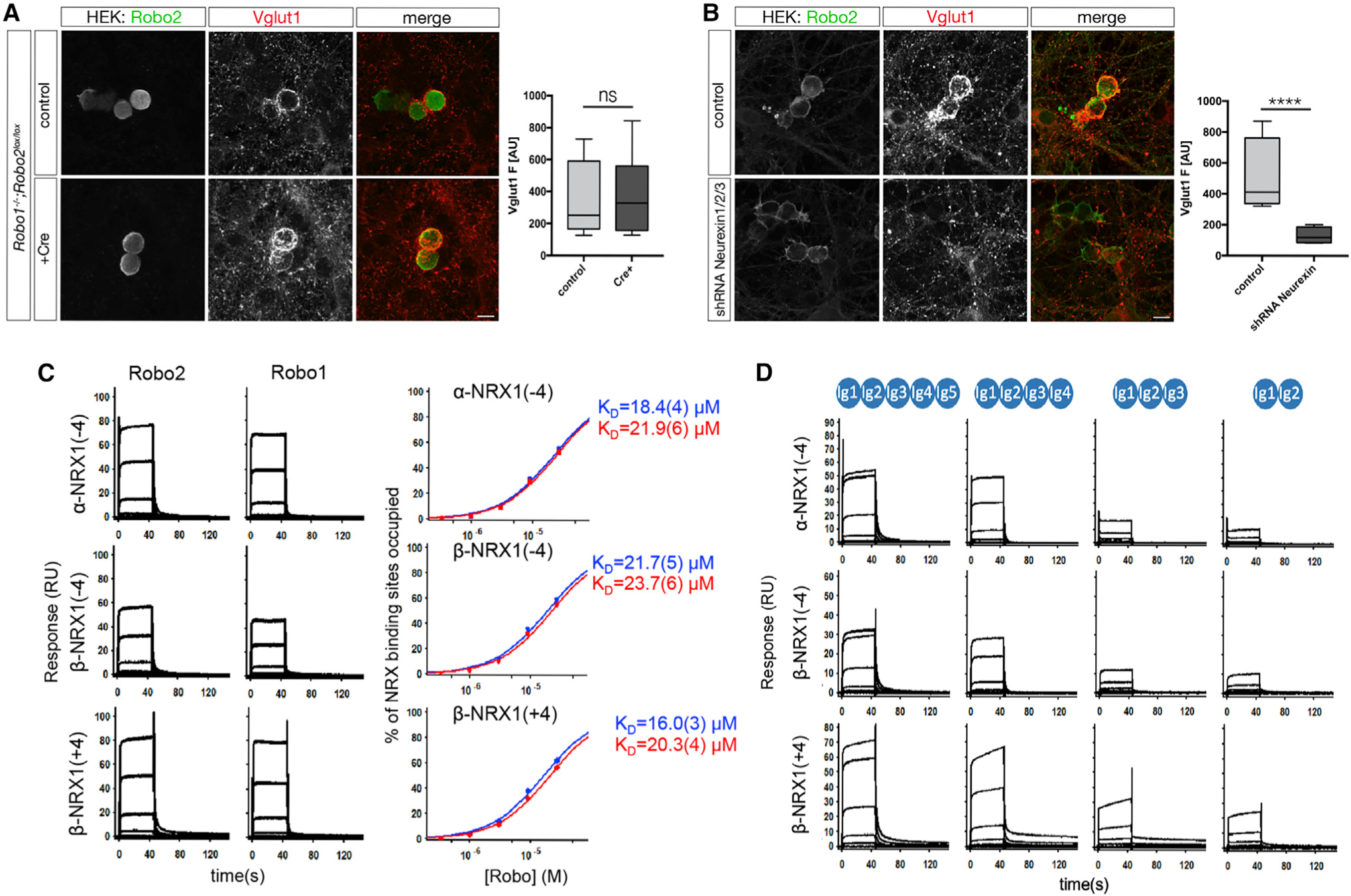
(A) Presynaptic Robo1/2 are not required for Vglut1 clustering around Robo2-expressing HEK293 cells. In vitro hemi-synapse assay was performed using primary neurons from either Robo1−/− or Robo1−/−;Robo2F/F (infected with Lentivirus expressing Cre-recombinase at DIV0, one-way ANOVA, ****p < 0.0001, ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05, whiskers show min/max, n = 3 independent experiments). Scale bar: 7μm.
(B) Presynaptic Neurexins are essential for Robo2-dependent Vglut1-clustering. In vitro hemi-synapse assay was performed in the presence (DIV3) of a Lentivirus expressing a pan-Neurexin shRNA. Neurexin knockdown completely abolishes Robo2-dependent Vglut1-clustering. Scale bar: 7μm.
(C) SPR binding experiments of Robo1 and Robo2 ectodomains over NRX surfaces: Binding of Robo2 and Robo1 (Ig1–5) over surfaces immobilized with α-NRX1Δ4, β-NRX1Δ4, and β-NRX1+4 ectodomains. Robo 2 and Robo1-binding was detected with all three NRX-immobilized surfaces. Binding isotherms of the percentage of NRX binding sites occupied versus Robo concentration (right panels) yield the KDs for Robo2 (Ig1–5) and Robo1 (Ig1–5), shown in blue and red, respectively. The number in brackets represents the error of the fit.
(D) Binding of Robo2 Ig deletion fragments over α-NRX1Δ4, β-NRX1Δ4, and β-NRX1+4 ectodomains. Robo2 fragments encompassing Ig domains 1–5, 1–4, 1–3 and 1–2 respectively were tested for binding. A sharp decrease in signal is observed between the Ig1–4 and Ig1–3 fragments suggesting that Nrxn binds mostly with the Ig4–5 domains of Robo2.
See also Figure S3.
