Fig. 6.
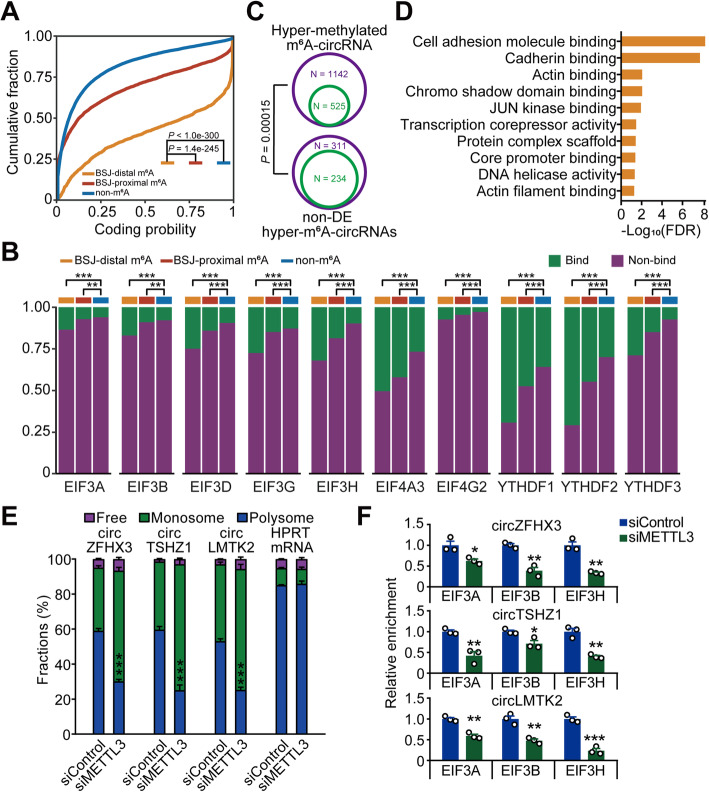
The hypermethylated m6A-circRNAs possess potential for translation. A The cumulative fraction of coding probability scores predicted by CPAT for BSJ-distal m6A-circRNAs, BSJ-near m6A-circRNAs and non-m6A-circRNAs. The P value was calculated with the Wilcoxon rank sum test. B Significant higher ratio of binding sites of EIFs and YTHDFs in BSJ-distal m6A-circRNAs than BSJ-near m6A-circRNAs and non-m6A-circRNAs. For each clustered bar, from left to right were binding sites ratios of BSJ-distal m6A-circRNAs, BSJ-near m6A-circRNAs, and non-m6A-circRNAs. P values were calculated by chi-squared test; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. C Venn diagram showing the number of m6A-circRNAs with coding potential (circRNAs with ORFs and EIFs binding sites) for non-DE hypermethylated-m6A-circRNA and all hypermethylated-m6A-circRNA. The outer layer indicated total number of corresponding m6A-circRNAs; the inner layer indicated the number of corresponding m6A-circRNAs with coding potential. Fisher’s exact test was used to derive the P value. D GO molecular function (MF) terms enrichment analysis for host genes of hypermethylated m6A-circRNAs with coding potential. E Relative fractions of unbound (free) RNAs, monosome- and polysome-bound RNAs for circZFHX3, circTSHZ1, and circLMTK2 in PDAC cell lines with METTL3 siRNA and control. The HPRT mRNA was used as control. F RIP-qPCR analysis showed EIF3A-, EIF3B-, and EIF3H-bound RNA abundance for circZFHX3, circTSHZ1, and circLMTK2 in PDAC cells with or without METTL3 knockdown. Data in E and F were means ± S.E.M. (n = 3). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, and P < 0.001 of Student’s t test comparing with each control