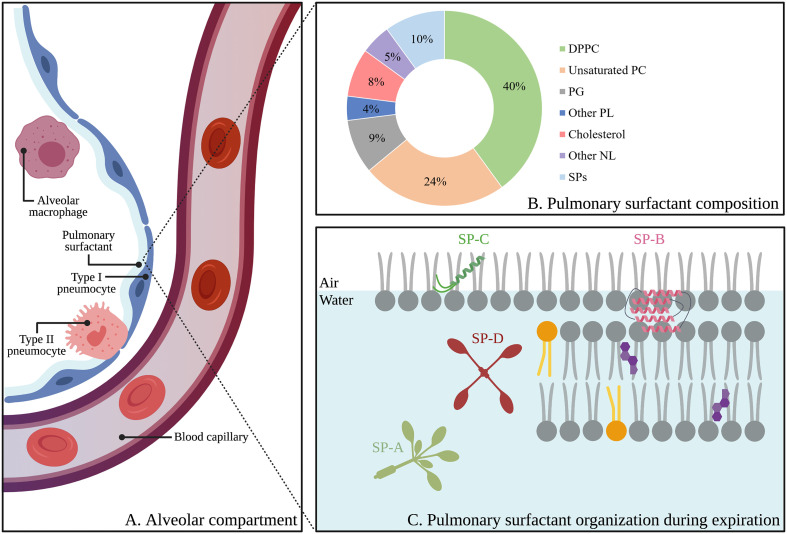
Fig. 2.
Schematic representation of the alveolar compartment, including the alveolar epithelium (i.e. type I- and type II pneumocytes), alveolar macrophages and pulmonary surfactant (A). Proteolipid composition of pulmonary surfactant (wt%) (B). Organization of pulmonary surfactant and lipid-protein interactions during expiration, according to the squeeze-out model. Grey, orange and purple lipids represent saturated lipids, unsaturated lipids and cholesterol, respectively (C). Abbreviations: DPPC; dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine, PC; phosphatidylcholine, PG; phosphatidylglycerol, PL; phospholipid, NL; neutral lipid, SPs; surfactant proteins, SP-A; surfactant protein-A, SP-B; surfactant protein-B, SP-C; surfactant protein-C, SP-D; surfactant protein-D. Created with BioRender.com (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)