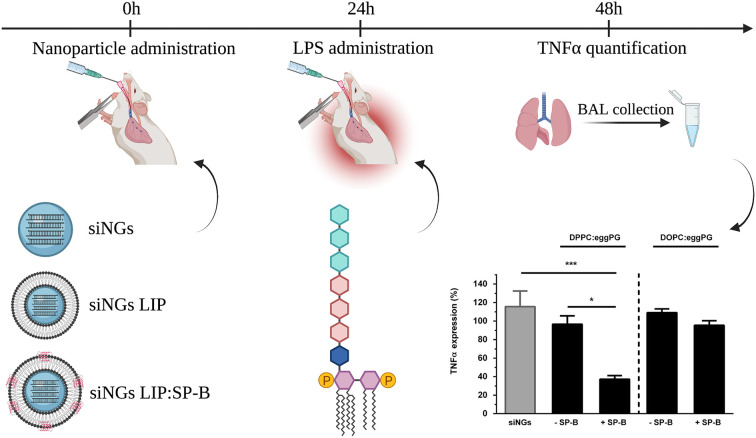
Fig. 6.
Schematic overview of relative TNFα silencing in a murine, LPS-induced acute lung injury (ALI) model. Intratracheal administration of anti-TNFα siRNA was performed using uncoated nanogels (siNGs) or nanogels coated with a surfactant-inspired proteolipid composition (DPPC or DOPC:PG 85:15, LIP), with or without SP-B (siNGs LIP, siNGs LIP:SP-B), followed by LPS administration after 24 h. TNFα levels were quantified in BAL fluid, obtained 24 h after LPS stimulation. TNFα expression levels of mice treated with anti-TNFα siRNA are normalized to mice treated with control siRNA (siCTRL). Only siRNA delivery using siNGs coated with DPPC:PG and supplemented with SP-B leads to substantial gene silencing. All values are a mean ± standard deviation (SD) from four independent repeats (n = 4). Statistical analysis was performed via One-Way ANOVA followed by a Tukey's multiple comparison test. Abbreviations: TNFα; tumor necrosis factor α, LPS; lipopolysaccharide, siNGs; siRNA-loaded nanogels, SP-B; surfactant protein-B, BAL; bronchoalveolar lavage. Data adopted from [49], with permission. Created with BioRender.com