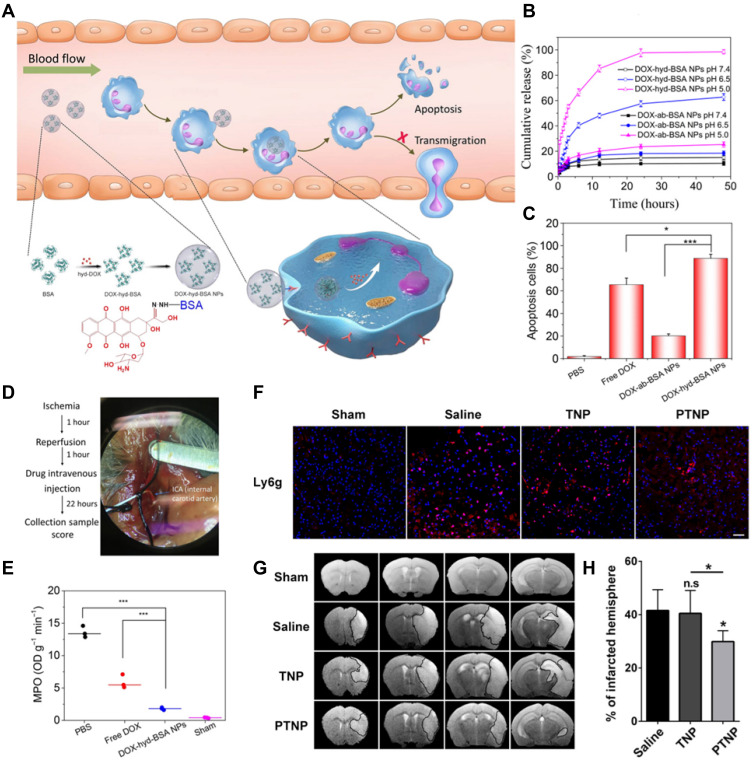
Figure 5.
(A) Scheme showing NP targeting of proinflammatory neutrophils to induce their apoptosis for treatment of inflammatory diseases. (B) Cumulative DOX release from DOX-ab-BSA NPs or DOX-hyd-BSA NPs in PBS at pH 7.4, 6.5, or 5.0. (C) Percentage of apoptotic cells analyzed by flow cytometry after HL-60 cells treated with various DOX formulations. (D) Experimental design to examine the benefit of DOX-hyd-BSA NPs in cerebral I/R. OD, optical density. (E) MPO activity in brain damage tissues at 22 h after administration of PBS, free DOX, and DOX-hyd-BSA NPs. Reproduced with permission from Zhang, CY, Dong, XY, Gao, J, Lin, WJ, Liu, Z, Wang, ZJ, Nanoparticle-induced neutrophil apoptosis increases survival in sepsis and alleviates neurological damage in stroke. Sci Adv 2019, 5 (11), eaax7964. Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).83 (F) CLSM images of neutrophil infiltration in ischemic brain regions after treatment with saline, TNPs, and PTNPs. Neutrophils were immunostained with anti-Ly6g antibody (red) and nuclei were stained using DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 50 μm. (G) T2-weighted images of ischemic brains at 24 h in tMCAO mice treated with saline, TNPs, and PTNPs. The black curve indicates the infarct region. (H) Quantification of the infarction volumes in saline-, TNP-, and PTNP-treated tMCAO mice. Error bars indicate SD (n = 5). Reproduced with permission from Tang CM, Wang C, Zhang Y, et al. Recognition, Intervention, and Monitoring of Neutrophils in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Nano Lett 2019, 19 (7), 4470–4477. Copyright μ 2019 American Chemical Society.84 *P < 0.05, and ***P < 0.001.