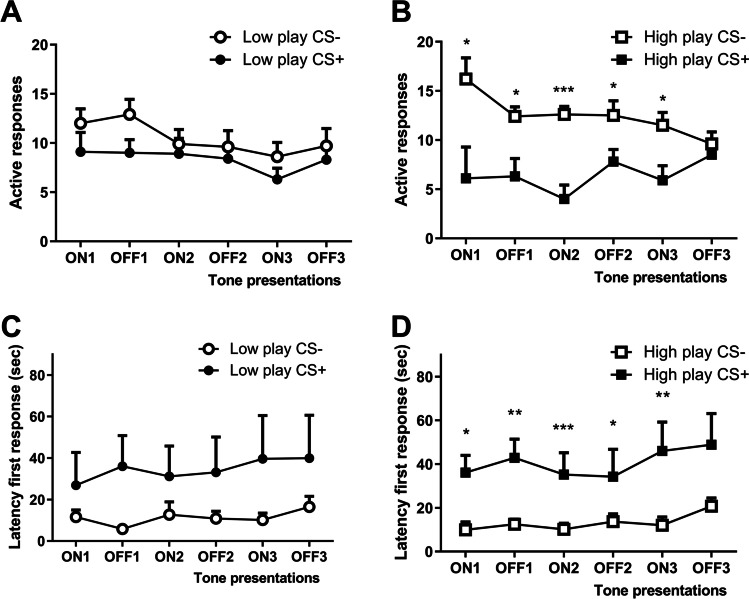
Fig. 4.
Conditioned suppression of alcohol seeking in low and high playing rats after 8 weeks of intermittent alcohol consumption. The number of active responses during consecutive CS-ON and CS-OFF intervals is shown for low players (A LP, CS − N = 9; CS + N = 7) and high players (B LP, CS − N = 13; CS + N = 16) that were control conditioned (CS −) or conditioned to associate a tone with footshocks (CS +). The latencies to the first active response during the CS-ON and CS-OFF intervals in low players (C LP, CS − N = 9; CS + N = 7) and high players (D LP, CS − N = 13; CS + N = 16), conditioned (CS +) and non-conditioned (CS −). Data are presented as mean + SEM active responses or latencies, binned in 2-min intervals. Significant differences between CS − and CS + subgroups are indicated by *, ** and *** (post hoc pairwise comparisons, p < 0.05, p < 0.01 and p < 0.001, respectively)