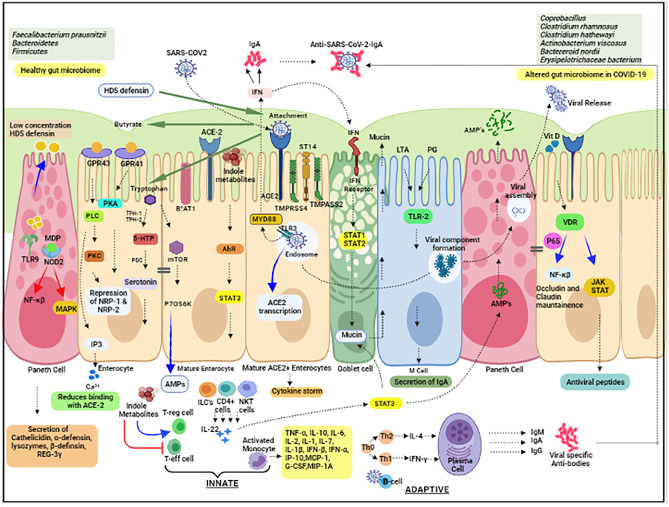
Fig. 3.
Modulation of innate and adaptive immunity by various postbiotics (schematic illustration depicting the action of various postbiotic molecules affecting innate and adaptive immunity) (red arrow representing the upregulation of various signaling pathways by various postbiotic molecules while blue arrow representing the downregulation of signaling pathways; green arrow representing the reduction of postbiotic molecules after binding of SARS-CoV-2 with ACE-2 receptor) ACE2, angiotensin-converting enzyme; B0AT1, amino acid transporter; NOD, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain2 (NOD-2); IDO, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; NKT, natural killer T; NRP-neuropilin; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; PKA, protein kinase A; HD-5, human defensin-5; GPRs, G-protein receptors; IL, interleukin; IFN, interferon; JAK/STAT, Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein,1; G-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; IP-10, interferon gamma-induced protein 10; MIP-1A, macrophage inflammatory protein,1; VDR, vitamin D receptor