FIGURE 1.
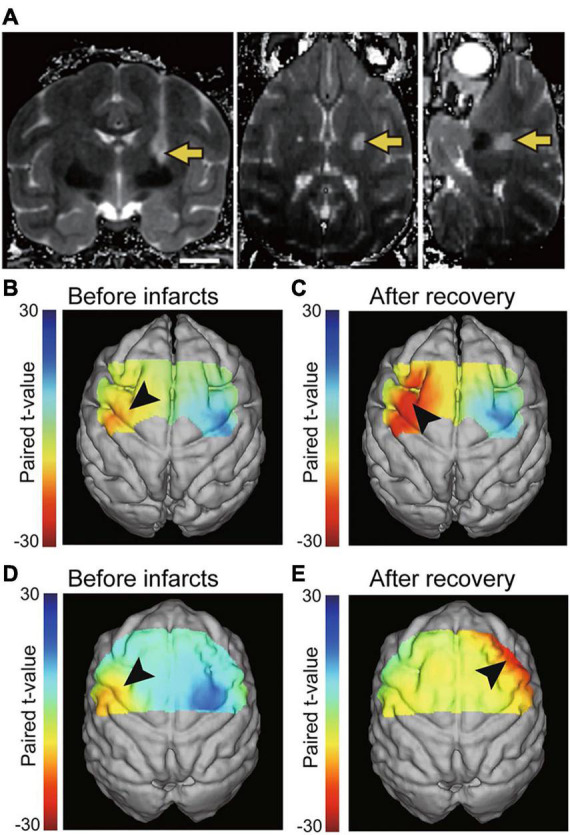
(A) T2-weighted MRI showing the location of infarcts in the posterior internal capsule one day after endothelin-1 injection (coronal, axial, and sagittal images). The arrows indicate the infarct. Scale bars = 10 mm. Reproduced from Figure 1 of the study by Murata and Higo (2016). (B–E) Brain activation during voluntary hand movements before infarcts (B,D) and after motor recovery from the internal capsular infarcts. Before infarcts, focal activation was observed in the hand area of the primary motor cortex (arrowhead in B,D). After motor recovery, increased activation of the premotor area was identified (arrowhead in C,E). The cortex contralateral to the stroke plays a greater role in recovery when lesions are more severe (E). Reproduced from Figures 2, 4 of the study by Kato et al. (2020b).
