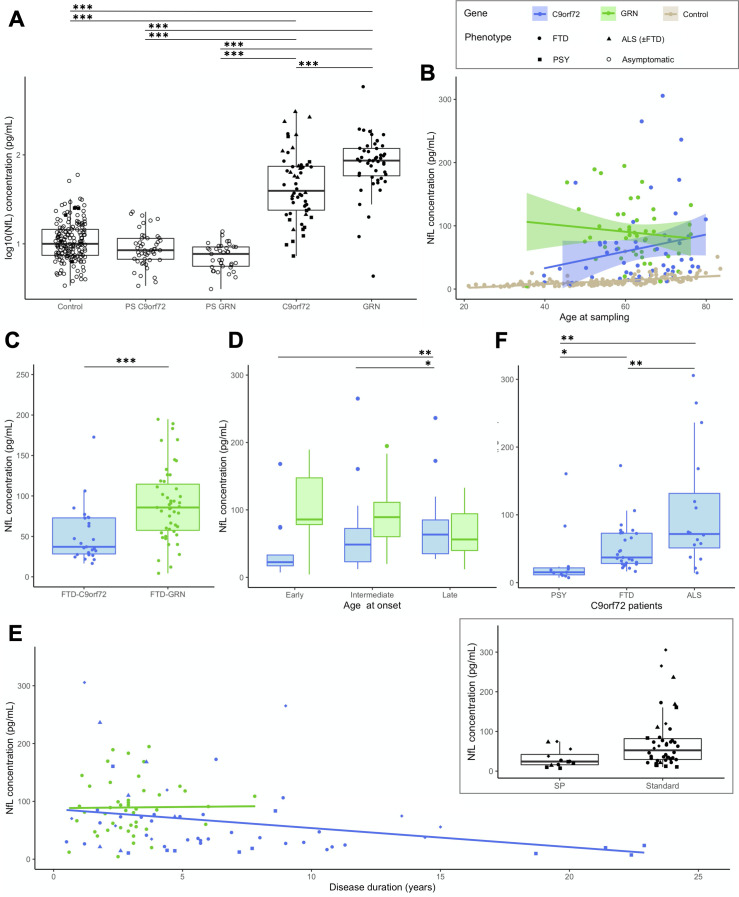
Figure 2.
Baseline pNfL levels in patients. (A) pNfL levels in C9orf72 and GRN patients compared with presymptomatic carriers and controls. (B) pNfL levels according to the age at sampling in C9orf72 (r=0.284, p=0.037) and in GRN (r=−0.123, p=0.406) patients, with controls displayed for comparison. (C) Comparison of pNfL levels between C9orf72 and GRN patients, restricting the analysis to those with FTD phenotype only. (D) Comparison of pNfL levels according to the age at onset, classified as early (before 50 years), intermediate (between 50 and 65 years) and late (after 65 years). Levels significantly differed in C9orf72 patients, but not in GRN patients. (E) pNfL levels according to disease duration, evidencing a negative correlation in C9orf72 patients (r=−0.311, p=0.021) but not in GRN patients (r=0.088, p=0.552). In the insert, C9orf72 carriers with atypical, SP disease course are compared with patients with standard disease duration. (F) Comparison of pNfL levels according to clinical phenotype in C9orf72 patients; patients with ALS were considered as a unique group, regardless of the presence of associated FTD. Asterisks indicate the significance of post hoc comparisons between the groups: *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. ALS, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; FTD, frontotemporal dementia; NfL, neurofilament light chain; pNfL, plasma neurofilament light chain; PSY, psychiatric presentations; SP, slowly progressive.