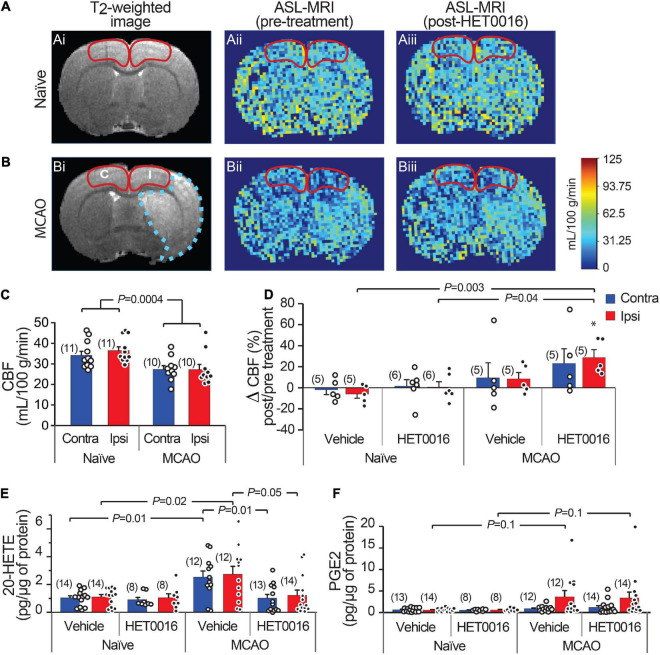
FIGURE 5.
Increased 20-HETE synthesis reduces resting CBF in the stroke peri-infarct. (A,B) T2-weighted MRI (left; Ai and Bi) and ASL images of CBF before (center; Aii and Bii) and after (right; Aiii and Biii) HET0016 injection in naïve and MCAO rats. CBF was quantified in the cortical regions outlined in red (I, ipsilateral peri-infarct; C, contralateral). (C) Cortical CBF is reduced bilaterally in MCAO animals compared to naïve animals. (D) HET0016 (1 mg/g i.v.) increases CBF significantly in the MCAO Ipsi peri-infarct region without altering CBF in naïve brains. (E,F) Mass spectrometric measurement of 20-HETE and PGE2 in microdissected cortical tissue (region marked in A,B), normalized to total protein. (E) 20-HETE is increased in both contralateral and ipsilateral cortices of MCAO rats and treatment with HET0016 reduces it to baseline levels comparable to naïve rats. (F) Cortical PGE2 levels are not changed significantly after MCAO and are not altered by HET0016 treatment. P-value in (C) was obtained from a two-way ANOVA. P-value in (D–F) was obtained from ANOVA followed by Tukey’s HSD. *indicates significantly different compared to zero change from baseline obtained from a one-sample T-test. Number in parentheses above each bar indicates N.