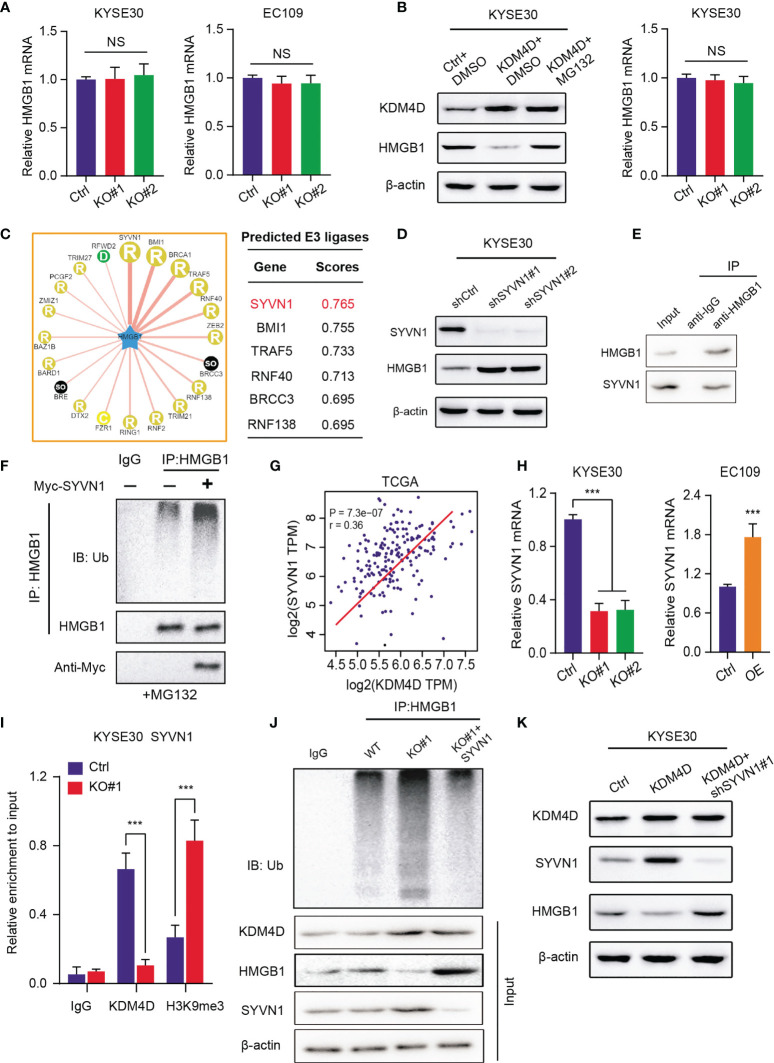
Figure 5.
KDM4D activates SYVN1 to promote HMGB1 degradation and restrict its protein levels. (A) Detection of HMGB1 mRNAs in Ctrl and KDM4D-KO cells (KYSE30 and EC109). (B) Detection of protein levels and mRNA levels of HMGB1 in three groups, including Ctrl+DMSO, KDM4D+DMSO and KDM4D+MG132. (C) Bioinformatic analysis for predicting E3 ubiquitin ligases that target HMGB1 for degradation based on the UbiBrowser dataset. (D) Western blot assays revealing the associations between SYVN1 and HMGB1. (E) Co-IP assay detecting the endogenous interactions between SYVN1 and HMGB1. (F) Western blot of the products of in vitro ubiquitination assays from 293 T cells transfected with the indicated plasmids and treated with 20 μM MG132 for 8 h. (G) Correlation analysis revealing the associations between KDM4D and SYVN1 mRNA levels in TCGA-ESCC cohort. (H) Detection of SYVN1 mRNA levels in different groups, as indicated. (I) The ChIP-PCR was conducted to confirm the occupancy of KDM4D and H3K9me3 modification at the SYVN1 promoter in KYSE30 cells. (J) Western blot of the products of in vitro ubiquitination assays from 293 T cells transfected with the indicated plasmids and treated with 20 μM MG132 for 8 h. (K) Western blot assays revealing the associations across KDM4D, STVN1 and HMGB1 in three groups, including Ctrl, KDM4D and KDM4D+shSYVN1#1. ***P < 0.001. NS, No Significance.