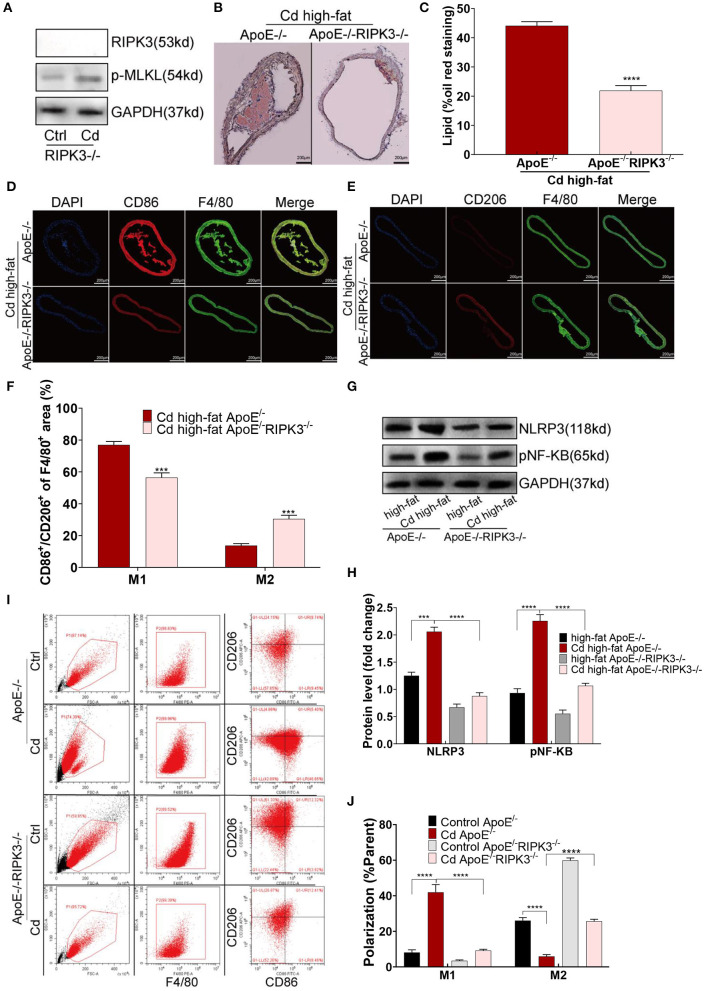
Figure 3.
Deletion of the RIPK3 inhibited polarity shift toward inflammatory macrophages and atherosclerosis. (A) The protein expression levels of RIPK3 and p-MLKL in the ApoE−/−/RIPK3−/−mice. (B) Representative photomicrographs of the aortic arch segments from the Cd- and high-fat-treated ApoE−/− or ApoE−/−/ RIPK3−/− mice stained with Oil Red O. (C) Quantification of the atherosclerotic lipid content. (D–F) Aortic arch of the Cd- and high-fat-treated ApoE−/− or ApoE−/−/ RIPK3−/− mice were probed with specific antibodies against the macrophage marker F4/80 and co-probed with antibodies against the markers of M1 (CD86) or the markers of M2 (CD206). (G,H) The protein expression levels of NLRP3 and pNF-KB in the aortic root of the ApoE−/− or ApoE−/−/ RIPK3−/− mice after treatment with Cd. (I,J) The polarization of BMDMs from ApoE−/− or ApoE−/−/ RIPK3−/− mice treated by Cd shown by flow cytometry (n = 5–7 per group). Data are shown as mean ± SD. ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.