Figure 1.
miR-216a is enriched in pancreatic islets and is highly conserved among various species
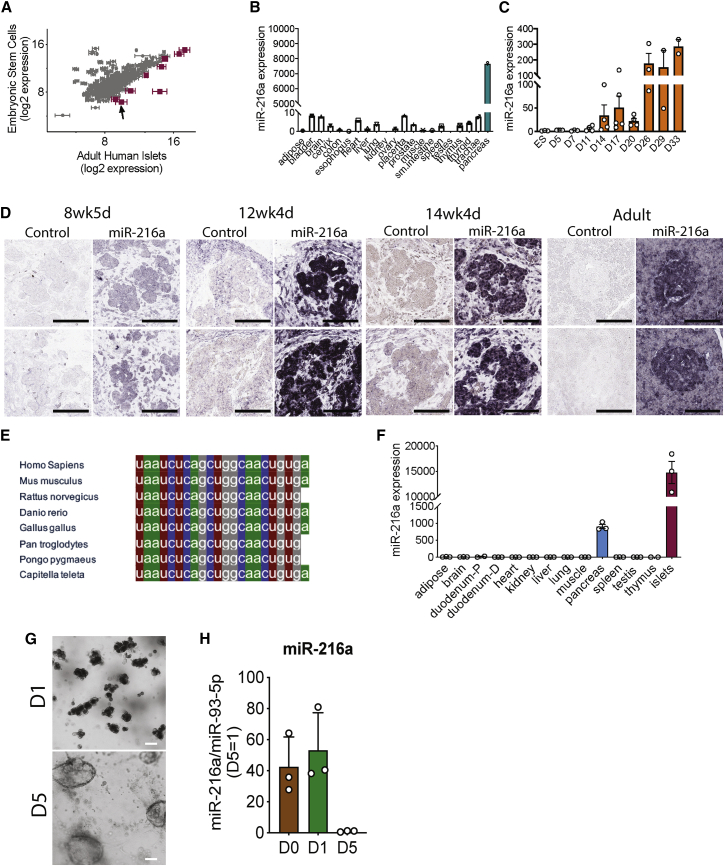
(A) miRNA profiling of adult human islets compared with human embryonic stem cells. miRNAs with greater than 3-fold increase in the islets are shown in magenta. Arrow points to miR-216a. n = 3 human islet donors. Data represent mean log2 signals ± SEM (from human islets).
(B) Equal amounts of RNA from various human tissues (each a pool of three tissue donors) was reverse-transcribed, and miR-216a expression was determined using qRT-PCR. Threshold cycle 33 (Ct = 33) was arbitrarily set as 1.
(C) Human embryonic stem cells (ESCs) were differentiated to pancreatic endocrine cells for the indicated days, and miR-216a expression was measured using qRT-PCR and expressed relative to levels in undifferentiated ESCs. In ESCs, Ct = 27.
(D) Fetal and adult human pancreata were probed with DIG-labeled miR-216a and scrambled control miRNA probes at the indicated gestational weeks. Purple color indicates presence of miRNA expression. Scale bar, 100 μm.
(E) Comparison of mature miR-216a sequences in different species.
(F) Same as in (B) except that the tissues were harvested from 8-week-old C57BL/6 male mice. n = 3 mice. Threshold cycle 33 (Ct = 33) was arbitrarily set as 1. Individual data points are shown in (C) and (F), and data represent mean ± SEM.
(G) Bright-field images of acinar cells differentiated toward ductal cells at day 1 (D1) and day 5 (D5) of differentiation. Scale bar, 100 μm.
(H) miR-216a expression was measured using qRT-PCR and normalized to miR-93-5p levels. Expression at day 5 is arbitrarily set as 1. At day 0, miR-216a Ct = ∼18.