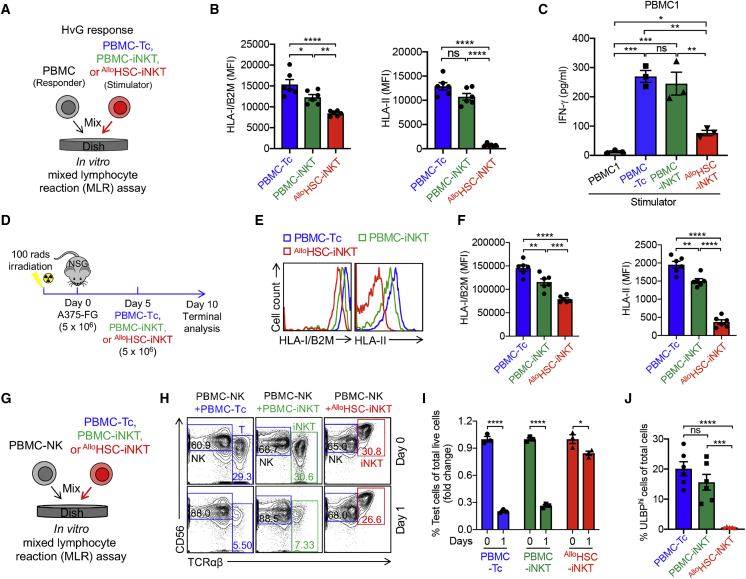
Figure 6.
Immunogenicity study of AlloHSC-iNKT cells
(A–C) Studying allogenic T cell response against AlloHSC-iNKT cells using an in vitro MLR assay. Irradiated AlloHSC-iNKT cells (as stimulators) were co-cultured with donor-mismatched PBMC cells (as responders). Irradiated PBMC-iNKT and PBMC-Tc cells were included as stimulator cell controls. (A) Experimental design. PBMCs from three different healthy donors were used as responders. (B) FACS analyses of HLA-I and HLA-II expression on the indicated stimulator cells (n = 6). (C) ELISA analyses of IFN-γ production at day 4 (n = 3).
(D–F) Studying HLA-I/II expression on AlloHSC-iNKT cells in vivo in an A375-FG human melanoma xenograft NSG mouse model. PBMC-iNKT and PBMC-Tc cells were included as effector cell controls. (D) Experimental design. (E) FACS analyses of HLA-I/II expression on the indicated effector cells isolated from A375-FG solid tumors. (F) Quantification of (E) (n = 5).
(G–J) Studying allogenic NK cell response against AlloHSC-iNKT cells using an in vitro MLR assay. AlloHSC-iNKT cells were co-cultured with donor-mismatched PBMC-NK cells. PBMC-iNKT and PBMC-Tc cells were included as controls. (G) Experimental design. (H) FACS analyses of the indicated cells at days 0 and 1. (I) Quantification of (H) (n = 3). (J) FACS analyses of ULBP expression on the indicated cells (n = 5–6).
Representative of two (D–F) and three (A–C and G–J) experiments. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. ns, not significant; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 by Student’s t test (I) or one-way ANOVA (B, C, F, and G). See also Figures S4–S6.