FIGURE 4.
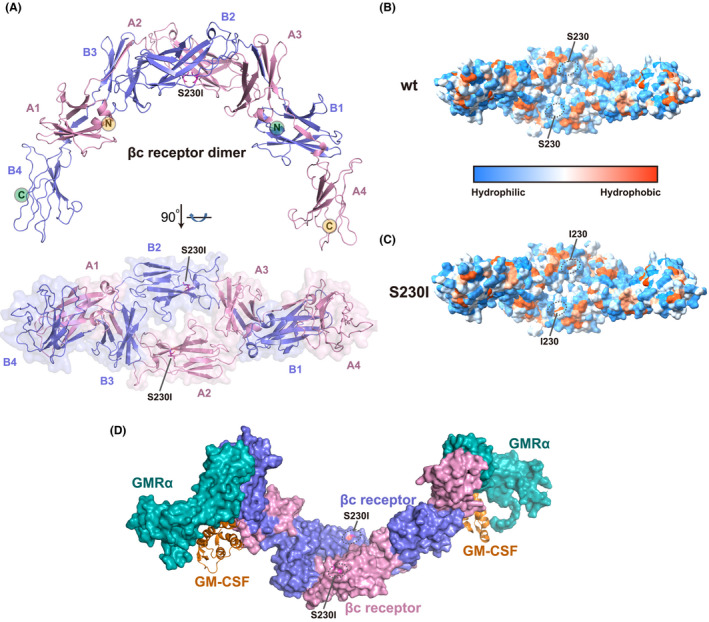
Cytokine βc receptor (CD131) S230I mutant protein structure and analysis. (A) Overall structure of βc receptor (CD131) S230I mutant protein homodimer. The S230I mutant structure was modeled by Swiss‐Model using the wild‐type structure (PDB: 1GH7) 22 as the template. The S230I residue was colored in magenta and highlighted by ligand shown. Two βc receptor molecules, colored by blue and pink, respectively, form a homodimer. The S230I mutation is located at the second domain of βc receptor. (B,C) Hydrophobic and hydrophilic surfaces of βc receptor wild‐type (B) and S230I mutant (C) protein homodimer. Hydrophobicity surfaces are presented by Chimera 23 with orange–red for most hydrophobic and dodger blue for most hydrophilic. The residue 230 is highlighted by black ellipses. S230I mutation contributes to more hydrophobic of the βc receptor dimer. (D) Superimposition of βc S230I mutant protein structure on the GM‐CSF/GMRα/βc ternary complex (PDB: 4NKQ). 24 Both GMRα and βc are shown on the surface. GMRα is colored in teal, and βc dimer is colored as panel A. GM‐CSF is shown in cartoon and colored in orange. The S230I mutation does not involve in the GM‐CSF and GMRα direct binding
