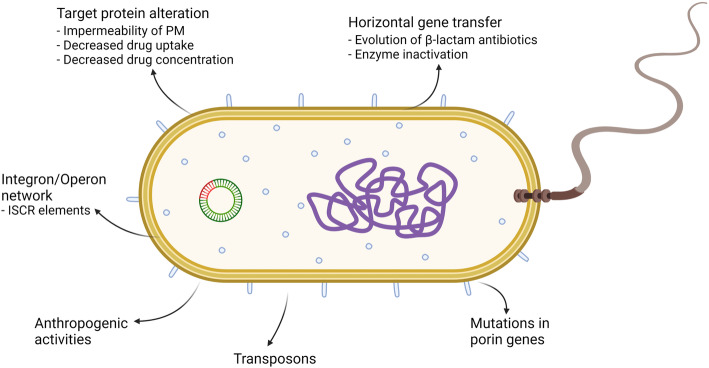
Fig. 1.
Drug resistance in bacteria. Target protein alteration. Certain modifications lead to impermeability of the cell membrane and thus decrease drug uptake. Target modification leads to a demoted drug binding. Integron Operon network. Integrons help insert a resistance gene at a pre-decided site downstream of a promoter (Example- Tn21). Anthropogenic activities. Release of toxic chemicals into the environment provides a selection and survival pressure which leads to variation and ultimately, evolution. Horizontal gene transfer. Transfer of genes from other species or from same species, but not parental cells is called HGT. Evolution of β-lactam antibiotic resistance genes is one of the results of HGT. Transposons. “Jumping genes” produces enzymes that aid in HGT. Mutation in porin genes. It can lead to decreased drug influx or increased drug efflux with the help of ion motive force, as compared to ATP hydrolysis by transporters