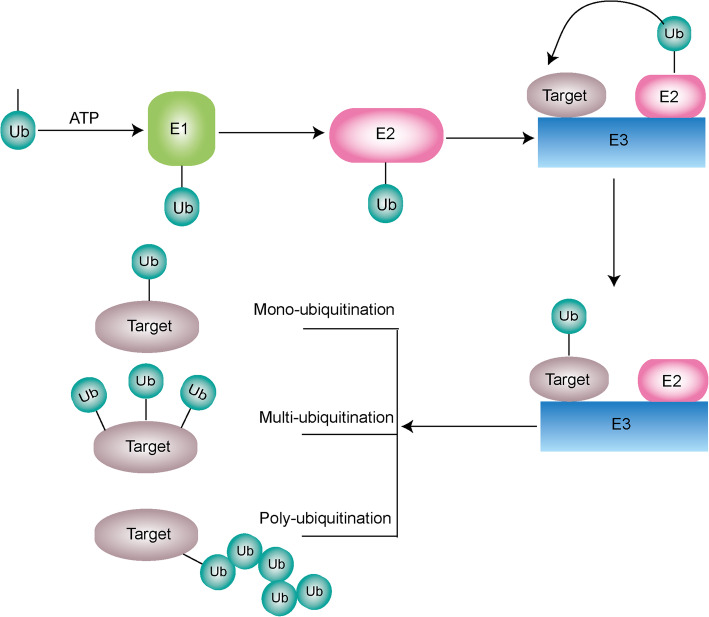
Fig. 2.
Overview of the cascade process of ubiquitination. Ubiquitination is an important cascade process of posttranslational modification catalyzed by three key enzymes. Firstly, E1 catalyzes the activation of Ub through a thioester bond in an ATP dependent mechanism. Then, activated Ub is transferred to the active-site cysteine residue of an E2. The last step is mediated by an E3 ligase that recognizes the E2 complex and facilitates the transfer of Ub from E2 to the target substrate. Due to the different binding style of Ub on the target substrate, types of ubiquitination modification are divided into three: mono-ubiquitination, multi-ubiquitination and poly-ubiquitination