Fig. 1.
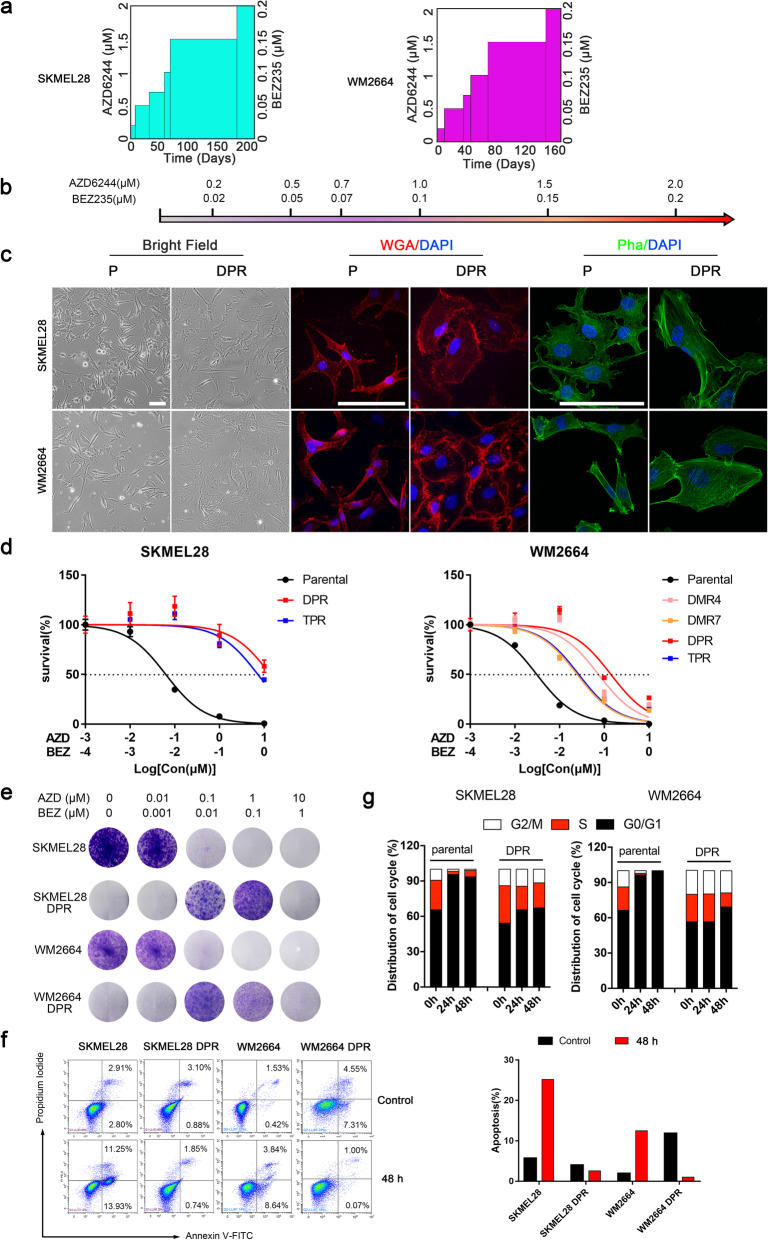
Chronic MAPK and PI3K dual-inhibition lead to acquired drug resistance. a Relative drugs exposure time to achieve resistance to MEKi+PI3K/mTORi in WM2664 and SKMEL28. b Drug naïve cells were chronically treated with increasing concentration of MEK inhibitor AZD6244 and PI3K/mTOR inhibitor BEZ235. c Phase-contrast images showing morphological changes in WM2664 and SKMEL28 parental and resistant cell lines (left), immunofluorescence staining for visualizing cell boundaries by fluorescence microscope (middle), immunofluorescence staining for cytoskeleton by confocal (right), (scale bar = 100 μm). d Survival curves of parental and dual-drug resistant cell lines titrated with the AZD6244 and BEZ235 or combine for 72 h. Results are shown relative to DMSO-treated controls (mean ± SEM, n = 5; dashed line, 50% inhibition). e Long-term colony formation assays of melanoma isogenic pairs. Parental and resistant clones were treated with indicated concentration of AZD6244 and BEZ235 for 12–14 days and then stained with 0.05% crystal violet to assay viability. The image is representative of three biological replicates. f Parental and DPR sublines were treated with DMSO or AZD6244 (1 μM) + BEZ235 (0.1 μM) for 48 h. Cells were collected and apoptosis was assessed via Annexin V-FITC staining. Quantification of the percentage of apoptosis cells (right). g Cell cycle analysis were assessed propidium iodide staining in parental and dual-drug resistant sublines treated with DMSO or AZD6244 (1 μM) plus BEZ235 (0.1 μM) for 24 or 48 h