Figure 1.
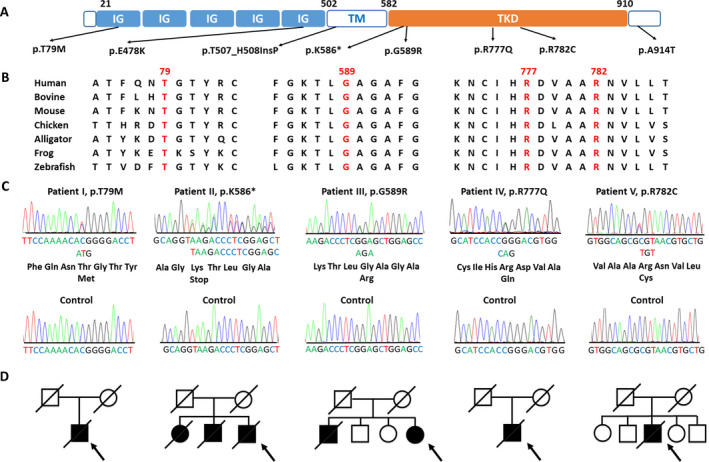
Genetic analysis of the CSF1R mutations identified in the Taiwanese patients with leukoencephalopathy. (A) Schematic illustration of the structure of CSF1R protein and position of the rare CSF1R variants identified in this study. IG = immunoglobulin‐like domain; TM = transmembrane domain; TKD = tyrosine kinase domain. (B) Alignment of multiple CSF1R protein orthologs showing evolutionary conservation of the amino acid residues altered by the putative pathogenic mutations. (C) Sanger sequencing trace demonstrating the five heterozygous CSF1R pathogenic mutations and corresponding wide‐type control sequences. (D) Pedigrees of the five index patients harboring a CSF1R pathogenic mutation. Open symbol: unaffected; filled symbol: affected; symbol with a diagonal line: deceased; arrow: proband; square: male; circle: female.
