Figure 2.
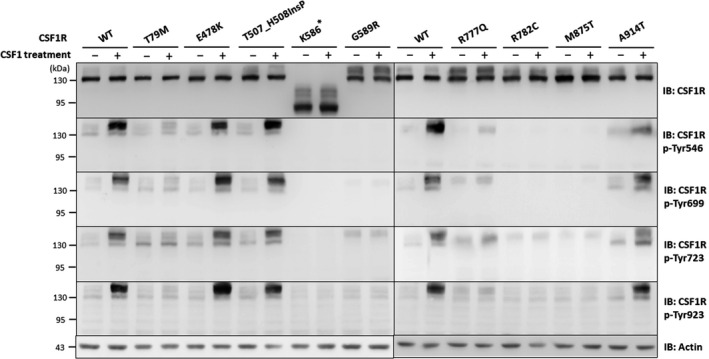
In vitro analysis of CSF1‐induced autophosphorylation of CSF1R mutant proteins. Representative western blots of lysates from HeLa cells that were transfected with wide‐type (WT) or mutant CSF1R expressing constructs with or without colony‐stimulating factor 1 (CSF1) treatment. Immunoblotting analysis using anti‐CSF1R antibody revealed comparable expression between WT and mutant CSF1R proteins. To evaluate the CSF1‐induced autophosphorylation activity of each CSF1R mutant, protein lysates were compared between CSF1‐treated and untreated cells expressing either one of the CSF1R mutant proteins. The five CSF1R mutants (T79M, K586*, G589R, R777Q, and R782C CSF1R) and the positive control M875T CSF1R had lost their ability to phosphorylate the Tyr546, Tyr699, Tyr723, and Tyr923 residues within CSF1R upon CSF1 stimulation, whereas the other three CSF1R mutants (E478K, T507_H508InsP, and A914T CSF1R) had preserved function of the CSF1‐induced autophosphorylation. Experiments were repeated three times with similar results. The equivalent amount of protein loading is shown using Actin as a loading control.
