Fig 3. MicroRNAs are regulators of cell fate during post embryonic development.
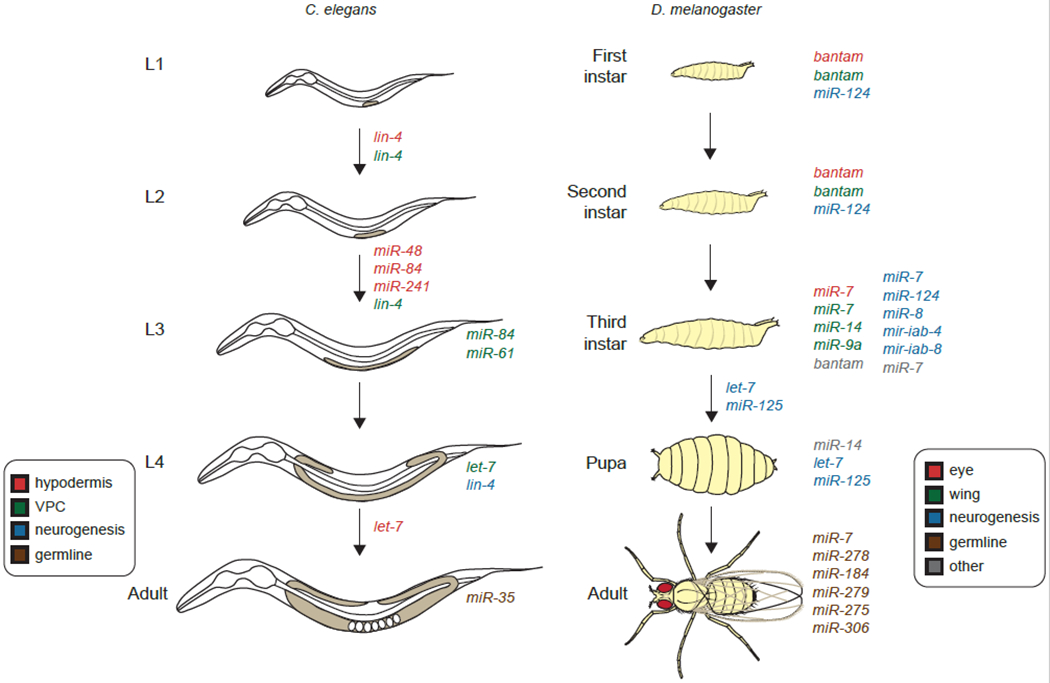
C. elegans L1 larvae undergo four molts before entering adulthood. MicroRNAs regulate differentiation in the hypodermis, vulval precursor cells (VPCs), neurons, and the germline in C. elegans. D. melanogaster first instar larvae undergo two larval molts, pupariation, and metamorphosis to form adults. MicroRNAs modulate cell proliferation and differentiation in the eye imaginal disc, wing imaginal disc, neurons, germline, glia, and salivary glands in D. melanogaster. The microRNAs indicated next to the arrows are key for developmental transitions, whereas, microRNAs indicated next to a developmental stage act during that stage.
