Figure 1. Trapping an activation-dependent complex between rhodopsin and GRK1.
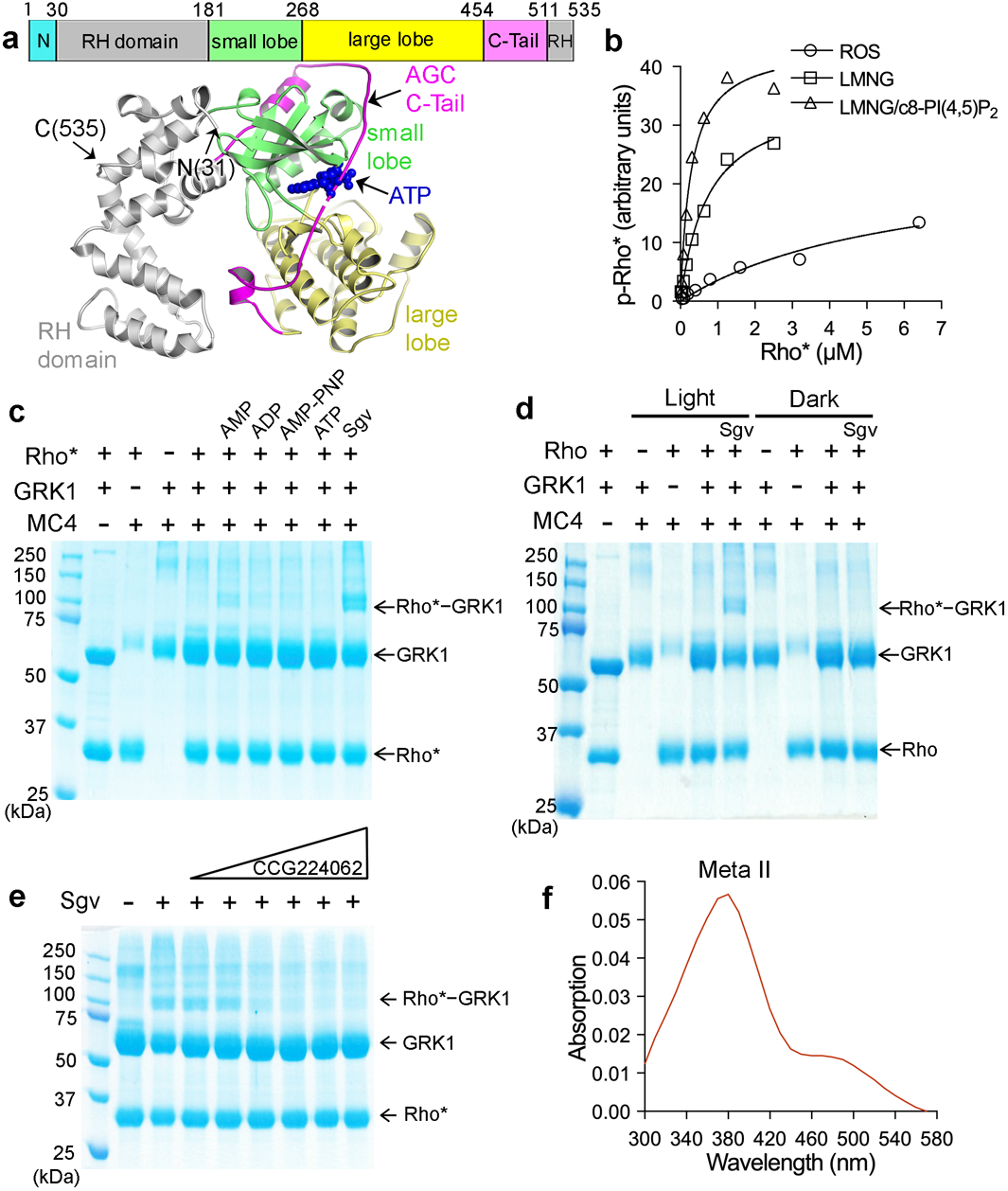
a) Primary structure of C-terminally truncated bovine GRK1 (residues 1–535) used in this study and its crystal structure in complex with ATP (PDB entry 3C4W45), wherein the N-terminus is disordered and the AST loop is partially ordered. b) Michaelis-Menten kinetics curves from a representative experiment out of three repeats with Rho* as substrate. Rhodopsin was solubilized with LMNG or LMNG/c8-PI(4,5)P2 and its kinetics was compared with rhodopsin in ROS. c) Crosslinking between Rho* and GRK1 in the presence of either 1 mM AMP, ADP, AMP-PNP, ATP, or 0.8 mM Sgv, an adenosine analog that helps stabilize the active conformation of GRKs. d) Light dependence of the crosslinking reaction. e) Crosslinking in the presence of Sgv was progressively inhibited by increasing amounts (10–630 μM) of the GRK inhibitor CCG224062 (IC50=0.1 nM)27, which stabilizes an inactive kinase domain conformation. For gel source data for c-e, see Supplementary Fig. 10a–c. f) The purified, crosslinked Rho*–GRK1 complex showed an absorption peak at 380 nm, consistent with Rho* stabilized in its Meta ll state.
