FIGURE 6.
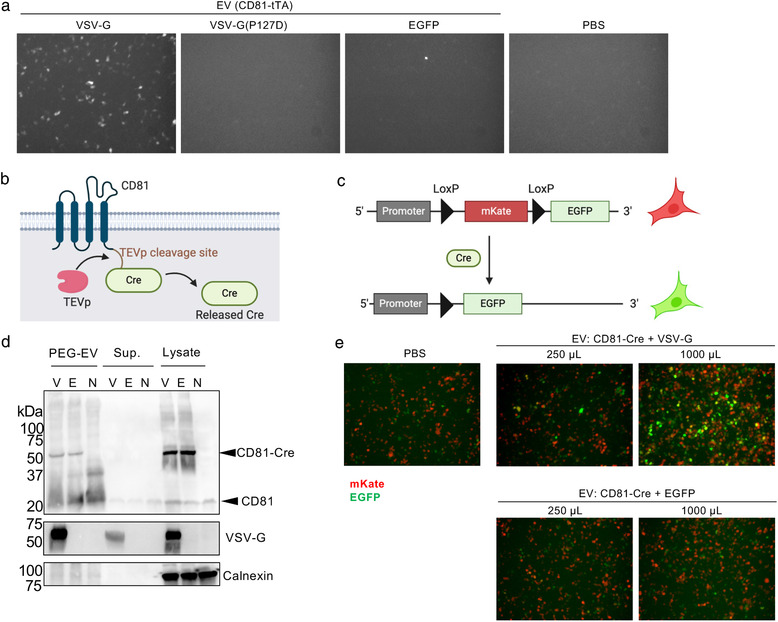
Fluorescence imaging‐based reporter assays. (a) EDDT assay based on EGFP as a reporter readout. Recipient HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding TRE3G‐EGFP and TEVp, and treated with EVs containing CD81‐tTA with VSV‐G (WT or P127D mutant) or EGFP (negative control). After 24 h, cells were observed under a fluorescence microscope. In this experiment, concentrated EVs corresponding to the 125 μl of crude supernatant was used. (b) Schematic representation of Cre‐fused CD81. (c) Schematic representation of reporter plasmid for Cre‐LoxP reporter assay. After the Cre cleavage, the mKate gene is excised and reporter cells become EGFP positive. (d) Western blotting analysis of donor EVs, supernatant, and cell lysate. Samples were run by non‐reducing SDS‐PAGE, transferred to the membrane, and probed by anti‐CD81 (upper), anti‐VSV‐G (middle), and anti‐calnexin (bottom) antibodies. V, CD81‐Cre + VSV‐G; E, CD81‐Cre + EGFP; N, no transfection. The expected mass based on the amino acid sequences were as follows: CD81‐Cre, 66.1 kDa; VSV‐G, 57.7 kDa; calnexin, 67.6 kDa (observed mass was approximately 90 kDa probably due to post‐translational modification). (e) Fluorescence imaging of Cre‐LoxP reporter assay. Recipient cells were treated with EVs harbouring CD81‐Cre with VSV‐G or EGFP. In this experiment, concentrated EVs equivalent to 250 or 1000 μl of crude supernatant were used
