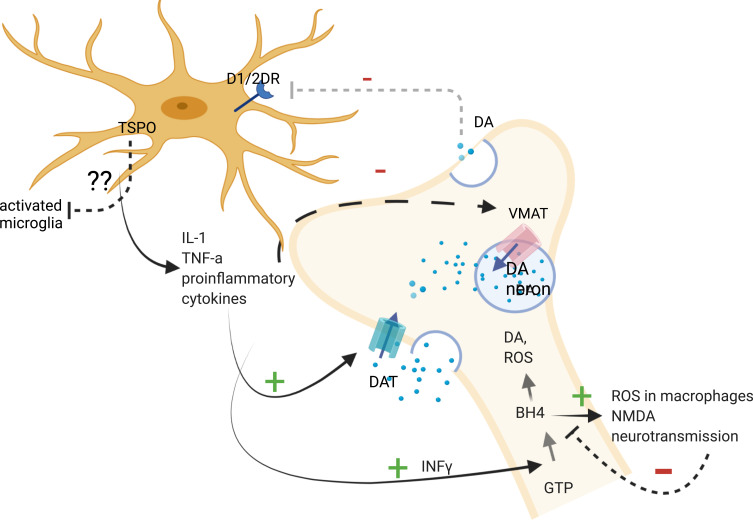
Figure 2.
Pathways between proinflammatory cytokines, dopaminergic neurons and microglia.
Notes: Proinflammatory cytokines have been shown to activate the biosynthesis of BH4, which is involved in the synthesis of dopamine and stimulates the production of reactive oxygen species in macrophages and NMDA neurotransmission. IL-1 and TNF have been associated with decreased expression of VMAT2. Pro-inflammatory cytokines have been associated with increased expression of DAT, which results in the elevation of cytoplasmic DA levels in neurons. Decreases in dopamine release may result in decreased dopamine-induced microglial inhibition. The role of TSPO on activated microglia where it is expressed remains to be established, but some studies suggested that it promotes anti-inflammatory microglial polarization. Created with BioRender.com.
Abbreviations: GTP, guanosine triphosphate; INFγ, interferon gamma; BH4, tetrahydrobiopterin; DA, dopamine; VMAT, vesicular monoamine transporter; DAT, dopamine transporter; ROS, reactive oxygen species; IL-1, interleukin-1; TNF-a, tumor necrosis factor-a; DRD1,2, dopamine receptor 1,2; dotted line/arrow, inhibition; arrows, activated pathway; +, activation; -, inhibition; ??, unknown. Image created with biorender.com.