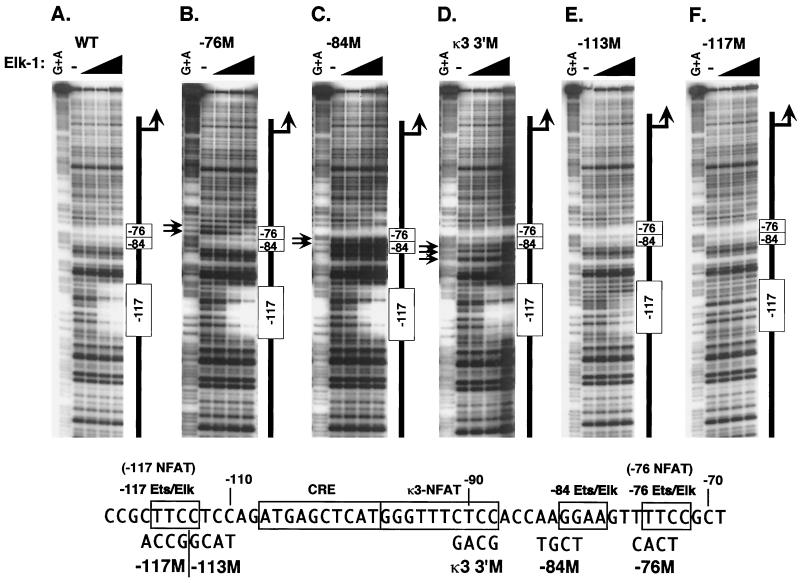
FIG. 7.
Mutation of the −76-NFAT, κ3-NFAT, −117-NFAT, or −84 sites in the TNF-α promoter inhibit Elk-1 binding. Quantitative DNase I footprinting using the wild-type human TNF-α promoter (nt −200 to +87 relative to the transcription start site) (A) or isogenic probes bearing mutations in the −76-NFAT site (−76M) (B), the −84 Elk-Ets site (−84M) (C), or the κ3 site (3′M) (D), as well as two mutations in the −117-NFAT site, −117M (E) and −113M (F), is shown. The sequences of the mutant sites are shown at the bottom of the figure. Probes were incubated with increasing concentrations of recombinant Elk-1 (50 ng, 200 ng, or 1 μg). Alterations in the cleavage pattern observed with the −76-NFAT and κ3-NFAT mutant templates in the vicinity of the −84 Ets-Elk site are indicated with arrows (B to D).