Figure 4: Two models for coordination between TLS and DSB Repair by REV7.
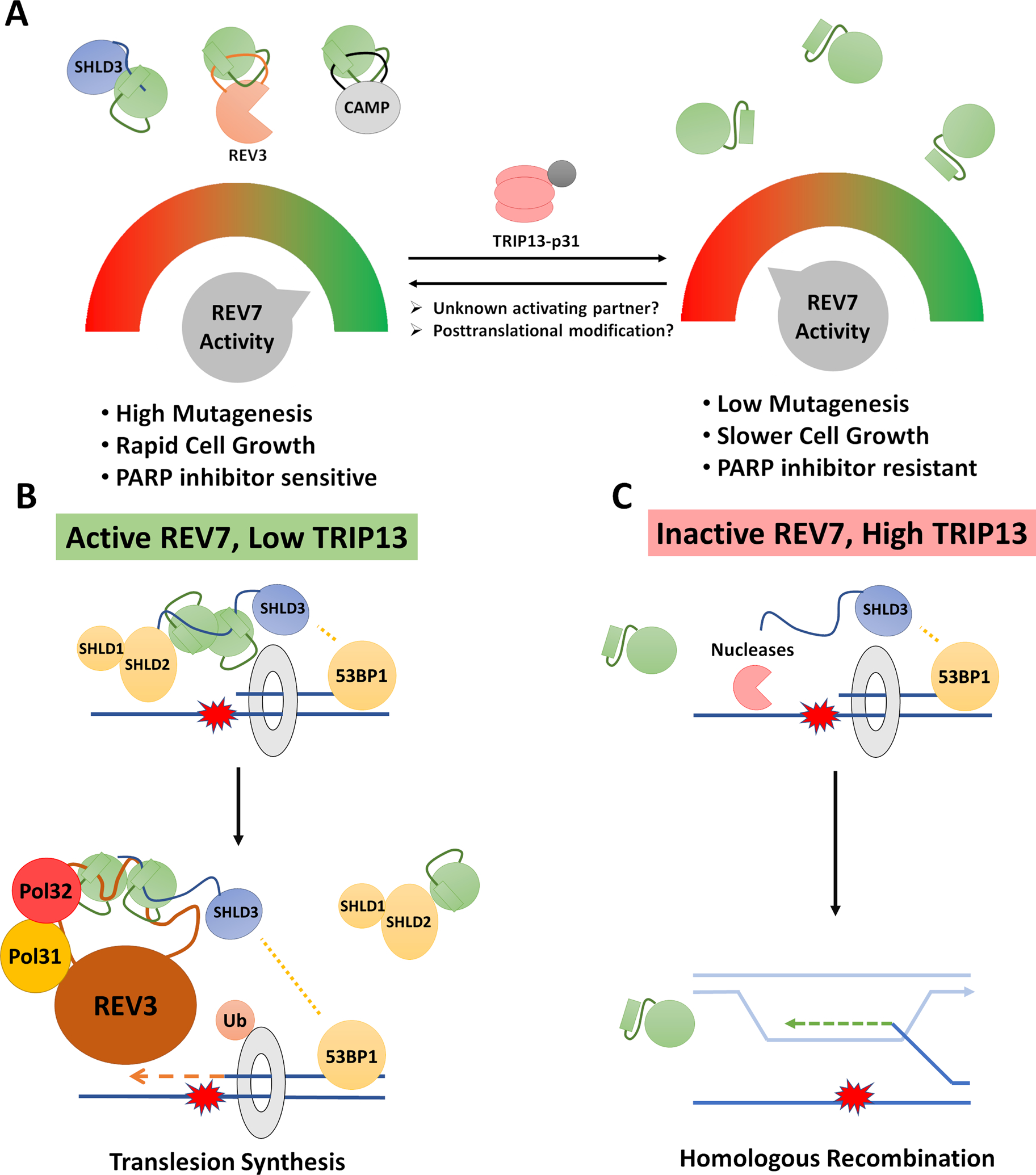
(A) Coordinate regulation: By modulating the activity of REV7, a cell can simultaneously coordinate two mutagenic DSB repair processes. This would provide the cell with a dial to exert significant control over mutagenic processes with a single signal. Such a dial could be adjusted based on cell type, cell cycle phase or external stimuli. It is also expected to be hijacked in cancer cells to either promote rapid growth and mutagenesis or resist chemotherapy. (B and C) Cooperation at stalled replication forks: translesion synthesis and double strand break repair factors are both known to act at certain types of stalled replication forks, hence direct interaction and cooperation between Shieldin and Polζ may be useful in this circumstance to inhibit homologous recombination and promote translesion synthesis. The ability of REV7 to interact with multiple partners simultaneously and form different types of homodimers allows for many possible higher order structures including hybrid Shieldin-Polζ complexes. While these have not been experimentally observed, they have not been ruled out. One such hypothetical hybrid complex is shown in (B).
