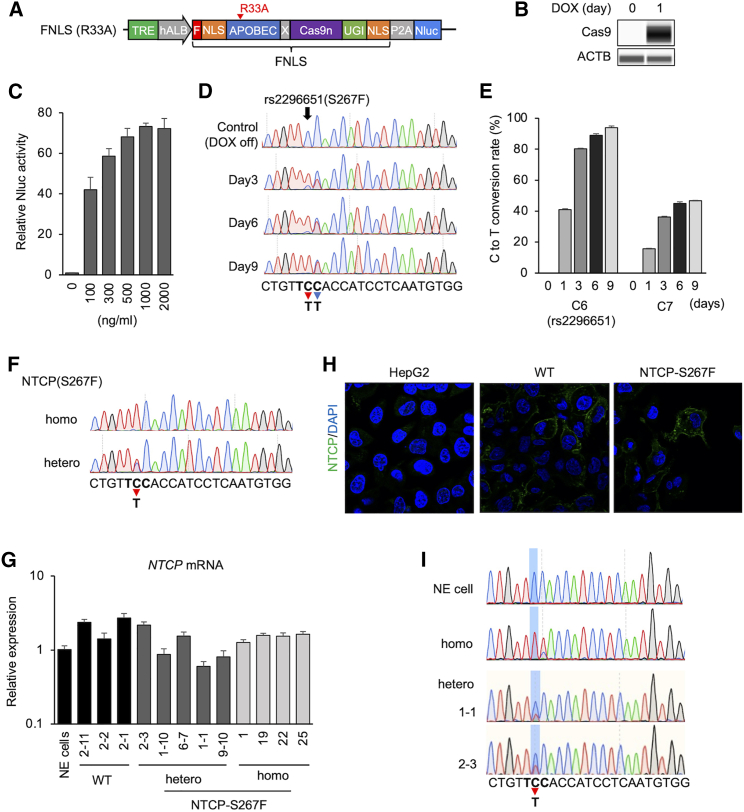
Figure 1.
Base editing of NTCP(S267F) in HepG2-NTCP cell and generation of HepG2-NTCP(S267F) cells
(A) Schematic representation of FNLS with APOBEC(R33A) mutation. The FNLS base editor carries a rat APOBEC cytidine deaminase at the N terminus of optimized Cas9n and a uracil glycosylase inhibitor (UGI) domain at the C terminus. Nuclear-localization signal (NLS) sequence is located at both the N terminus (with an FLAG epitope tag) and the C terminus. (B) Western blotting of Cas9 in HepG2-NTCP/FNLS(R33A) cells treated with Dox (500 ng/mL) for 1 day or untreated (0 day). (C) Nluc assay in HepG2-NTCP/FNLS(R33A) in different Dox concentrations. (D) Base editing on target site after Dox treatment in HepG2-NTCP/FNLS(R33A)/SLC10A-sgRNA. Sequence around the SLC10A-sgRNA rs2296651 is shown below. Bold letters represent the amino acid codon for S267F. Red arrow and blue arrow show C6 (rs2296651) and C7 position with editing to T, respectively. (E) Frequency (%) of C-to-T conversion on C6 and C7 in HepG2-NTCP/FNLS(R33A)/SLC10A-sgRNA after Dox treatment. (F) Sequence of selected homozygous and heterozygous clone of NTCP(S267F). (G) NTCP mRNA expression in selected HepG2-NTCP(S267F) clones. Non-edited (NE) cell is HepG2-NTCP/FNLS(R33A)/SLC10A-sgRNA without Dox treatment. (H) Immunostaining of NTCP in HepG2-NTCP(WT) and HepG2-NTCP(S267F) shows expression and membrane location of NTCP in HepG2-NTCP(WT) and -NTCP(S267F). (I) RNA was extracted from NE cells, homozygous and heterozygous clones, and subjected to RT-PCR and sequence determination. Quantitative data are shown as means ± standard deviation of triplicates.