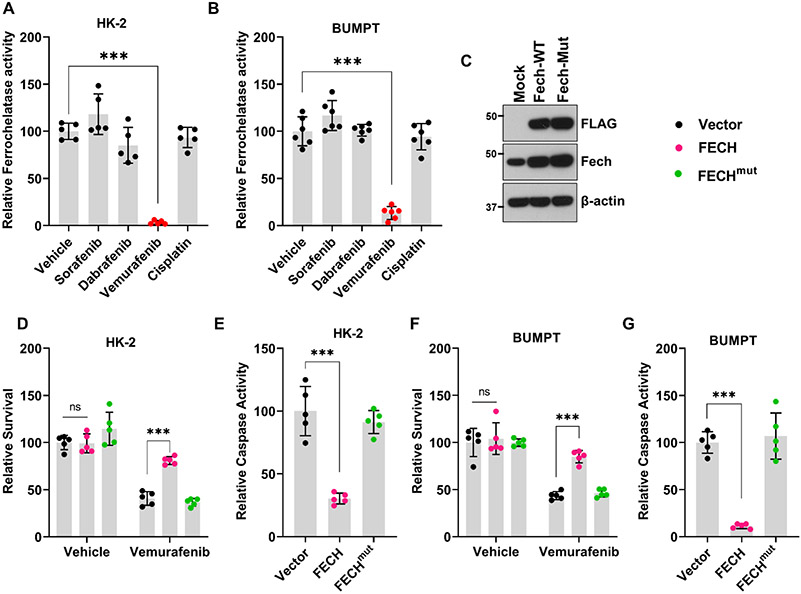
Figure 4: Ferrochelatase inhibition contributes to Vemurafenib mediated RTEC cell death.
Tubular epithelial cell lines of murine (BUMPT) and human (HK-2) origin were treated with vehicle, cisplatin or kinase inhibitors including vemurafenib at 50 μM concentration, followed by assessment of ferrochelatase activity at 24 hours. (A-B) Ferrochelatase activity was inhibited by vemurafenib in BUMPT and HK-2 cells. (B) Representative immunoblot showing overexpression of FLAG-tagged wild type and mutant FECH. Blots are representative of three independent experiments. (D-G) Empty vector, wild type FECH, or FECH mutant (M98K) was overexpressed in BUMPT (transient transfection) and HK-2 (lentiviral transduction) cells followed by treatment with either vehicle or 50 μM vemurafenib for 48 hours. Trypan blue based survival assays and caspase assays showed that wild type FECH overexpression can protect BUMPT and HK-2 cells from vemurafenib-associated cell death. In all the bar graphs (n=5-6 biologically independent samples) from one out of three independent experiments, all producing similar results, and experimental values are presented as mean ± s.d. The height of error bar = 1 s.d. and p < 0.05 was indicated as statistically significant. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple-comparison test was carried out and statistical significance is indicated by *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.