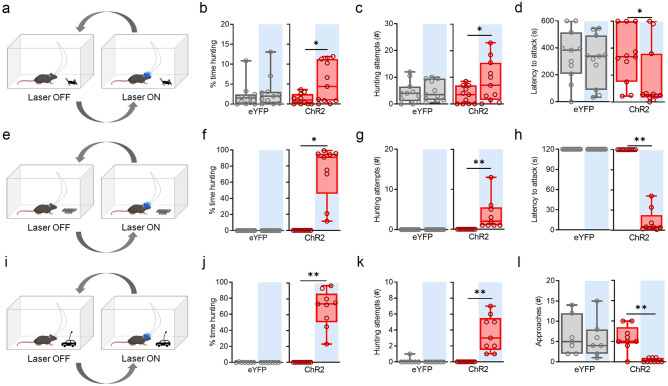
Figure 4.
BFGAD2+ activation promotes hunting of live and artificial prey. (a) Design of live cricket prey hunting assay used in (b–d). (b) Percent time hunting, defined as the time spent pursuing and capturing the cricket. ChR2, Wilcoxon signed rank test, W = 43, *p < 0.05. ChR2, n = 11; eYFP, n = 11. (c) Number of hunting attempts. ChR2, paired t-test, t10 = 2.36, *p < 0.05. ChR2, n = 11, eYFP, n = 11. (d) Latency to attack. ChR2, Wilcoxon signed rank test, W = − 43, *p < 0.05. (e) Design for artificial prey hunting assay used in (f–h). Artificial prey consisted of a small toy (robobug) that is propelled by vibration. (f) Percent time hunting. ChR2, Wilcoxon signed rank test, W = 45, **p < 0.01. ChR2, n = 9; eYFP, n = 14. (g), Number of hunting attempts. ChR2, Wilcoxon signed rank test, W = 45, **p < 0.01. (h) Latency to attack. ChR2, Wilcoxon signed rank test, W = 45, **p < 0.01. (i) Design of the interactive artificial prey assay used in (j–l). Interactive prey consisted of a toy car remote-controlled by the experimenter. (j) Percent time hunting. ChR2, Wilcoxon signed rank test, W = 45, **p < 0.01. ChR2, n = 9; eYFP, n = 7. (k) Number of hunting attempts. ChR2, Wilcoxon signed rank test, W = 45, **p < 0.01. ChR2, n = 9; eYFP, n = 7. (l, Number of approaches to the toy car. ChR2, Wilcoxon signed rank test, W = 45, **p < 0.01. ChR2, n = 9; eYFP, n = 7. Schematics (a,e,i) were created using BioRender.com and PowerPoint.