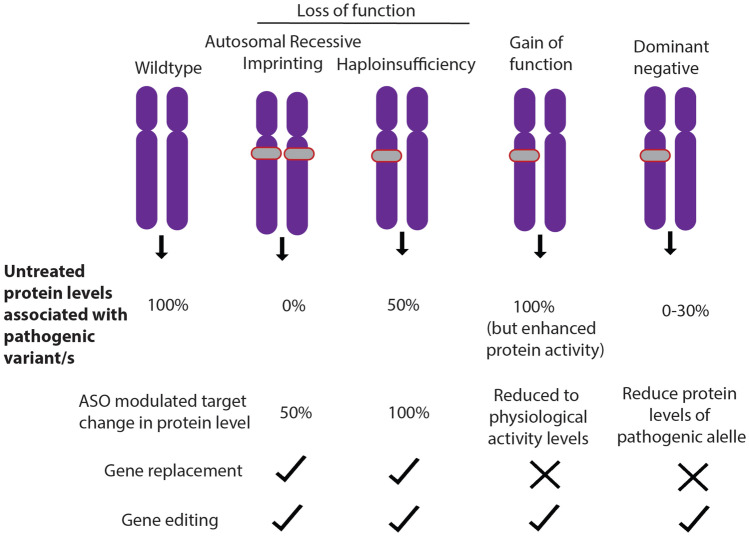
Fig. 1.
Pathogenic mechanisms and precision therapy approaches in the monogenic epilepsies. Autosomal recessive disorders result in no functional protein as pathogenic variants occur on both alleles (grey). Likewise, imprinting disorders result in no functional protein due to a pathogenic variant on one allele, while there is no protein from the imprinted allele. Gain-of-function variants can both increase protein function, or alter the protein function, often in a toxic manner. Dominant negative variants interfere with the functional protein made from the other allele resulting in less than 50% residual protein. The viable ASO approach is shown as well as whether this pathogenic mechanism can be targeted using gene replacement or editing