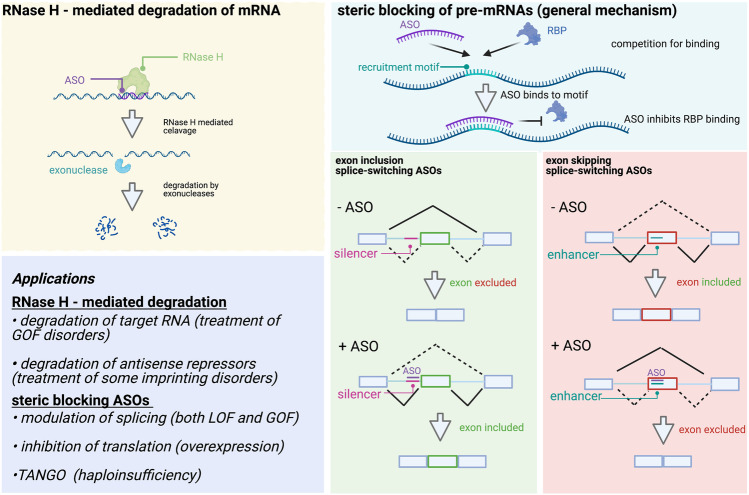
Fig. 2.
Mechanisms of gene regulation by ASOs. Left: RNase H–mediated regulation occurs by ASO binding and RNase H recruitment which cleaves the RNA component of DNA:RNA duplexes. The products of this cleavage are then further degraded by exonucleases, leading to reduced RNA and protein levels. Top right: General mechanism of steric blocking ASOs. ASOs compete for regulatory motifs that serve as RNA-binding protein (RBP) recruitment sites. ASO binding inhibits binding of regulatory RBPs by masking the recognition sequence. Bottom right: Examples of mechanisms by which ASOs can promote exon inclusion by masking silencer regions (left), or promote exon skipping by masking splicing enhancer regions (right). Bottom left: Applications of RNase H and steric blocking ASOs