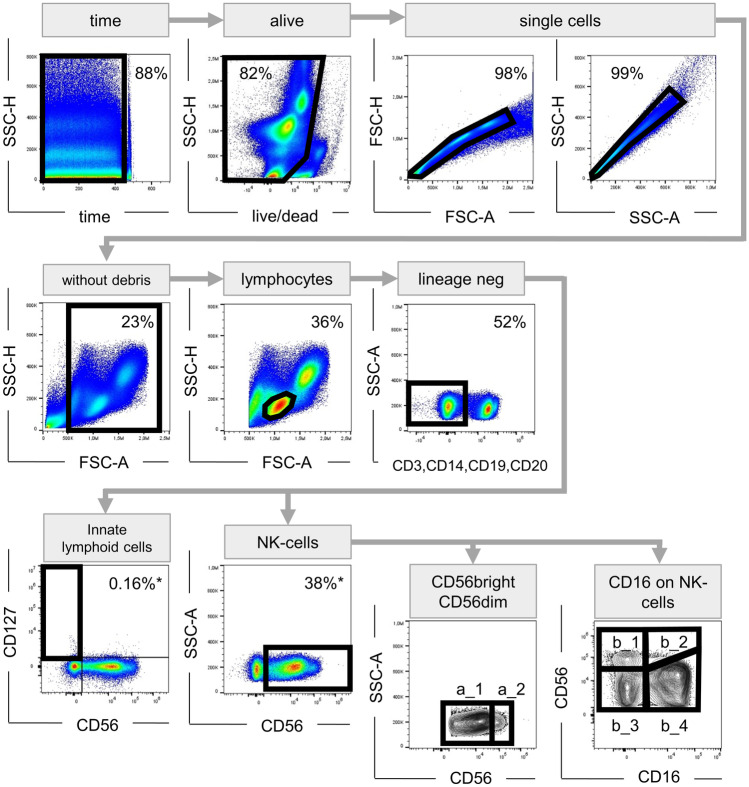
Fig. 1.
Gating strategy. Artefacts caused by poor flow were eliminated in a time vs. scatter plot; afterwards, dead cells as well as cell clumps or doublets were excluded; to disregard cell debris, only events > 500,000 on the FSC-A scale were included in further analysis; lymphocyte population was determined by its characteristic morphology in FSC-A vs. SSC-H plot; T, B, NKT cells and monocytes were excluded from the analysis by staining for CD3, CD19, CD14, or CD20, respectively. ILCs were described as lineage-negative, CD56−CD127+ cells. NK cells were defined as lineage-negative CD56+ cells. The CD56+ cells were further discriminated in CD56dim (a_1) and CD56bright (a_2) cells. The expression of the other markers of interest (CCR7, NKG2C, DNAM-1, CD158a/h, NKG2A, CD94, NKG2D, CX3CR, NKp46) were analysed considering both, all NK cells and the subgroups (CD56dim and CD56bright). NK cells were also subcategorized according to CD16 expression in CD56brightCD16− (b_1), CD56brightCD16+ (b_2), CD56dimCD16− (b_3), and CD56dimCD16+ (b_4). FSC forward scatter, SSC side scatter, -H pulse height, -A pulse area