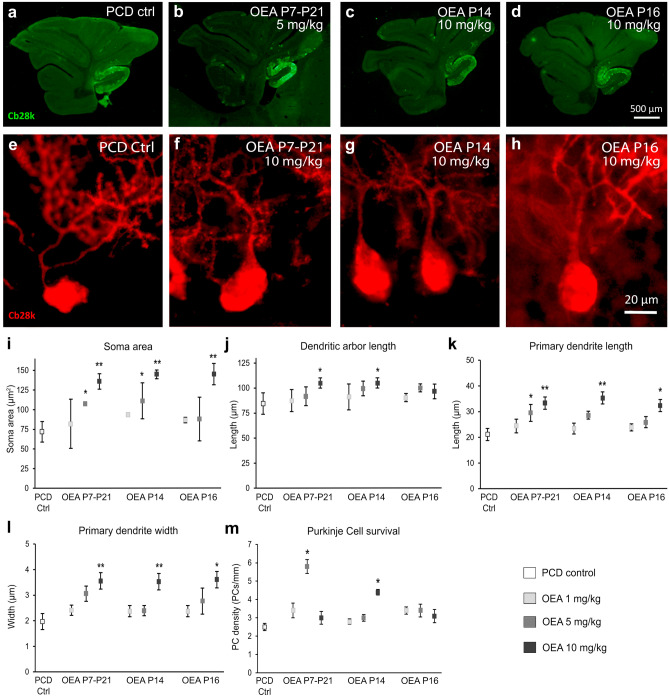
Fig. 3.
In vivo effect of different OEA dosages on the morphology and survival of the Purkinje cells of the PCD mouse analyzed at P30 (first set of experiments). (a–d) Micrographs of PCD cerebellar vermis slices labeled with calbindin (Cb28k, green) after different OEA treatments: control (a), chronic administration from P7 to P21 of 5 mg/kg (b), acute administration of 10 mg/kg at P14 (c), acute administration of 10 mg/kg at P16 (d). (e–h) Micrographs of Purkinje cells labeled with calbindin (Cb28k; red) in PCD animals treated with different dosages of OEA: control (e), chronic administration from P7 to P21 of 10 mg/kg (f), acute administration of 10 mg/kg at P14 (g), acute administration of 10 mg/kg at P16 (h). (i–l) Quantification of the OEA effect on different morphological parameters of PCD Purkinje cells; note that the chronic and acute administration at P14 have a stronger neuroprotective effect than the acute administration at P16 in all the parameters evaluated. (m) Quantification of PCD Purkinje cell survival at different OEA dosages; note that both chronic administration at a dose of 5 mg/kg and acute administration at P14 at a dose of 10 mg/kg prevented Purkinje cell death. Data are represented as mean ± SEM; n = 4 each experimental group; one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post hoc test for (i-m) * p < 0.05; **p < 0.01