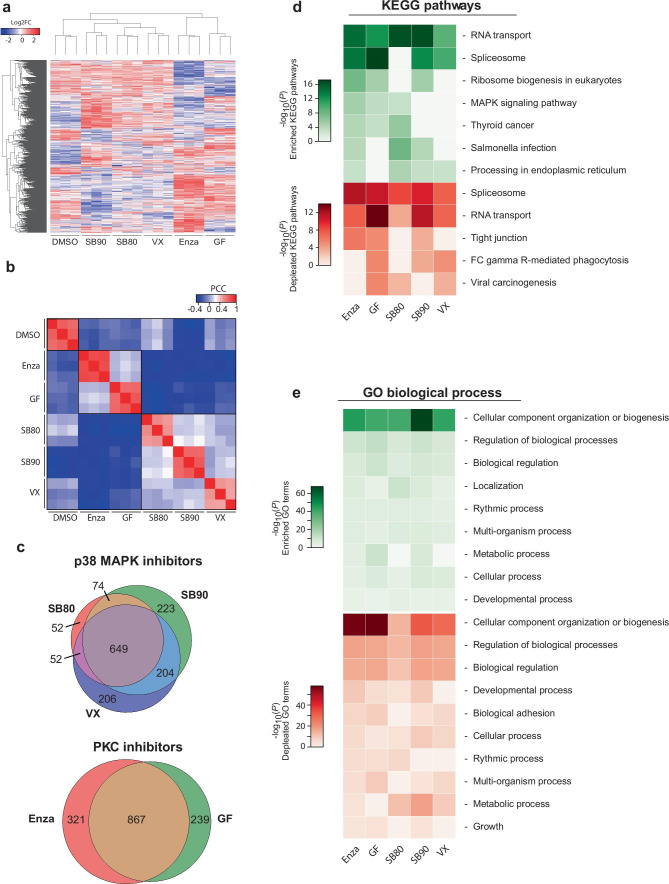
Fig. 4.
Phospho-proteome shows alterations in protein translation and cellular component organization/biogenesis following inhibitor treatment. a Unsupervised clustering of altered phospho-proteome (log2FC) group samples correctly based on target pathways. b Reproducibility between replicates and similarity among inhibitors with the same targets give rise to defined clusters based on PCC. c Contrasting the altered phospho-proteome depending on inhibitor target shows a high degree of overlap, with 44.5% for p38 MAPK and 60.8% for PKC. d, e Functional analysis using DAVID of the altered phospho-proteome identified two main processes depending on the analysis employed. d KEGG analysis indicated the main alterations, both for increased (green) and decreased (red) phosphorylation being RNA transport and spliceosome. In contrast, GO analysis displayed only one major profile found in both negatively and positively altered, being cellular component organization and biogenesis