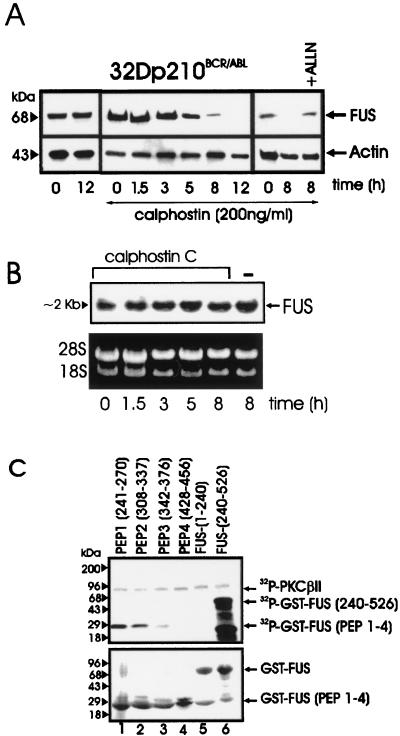
FIG. 3.
PKC-dependent FUS expression and identification of FUS PKCβII phosphorylation sites. (A) Western blot of FUS expression in BCR-ABL-expressing 32Dcl3 cells untreated or treated for the indicated times with calphostin C, alone or in the presence of the proteasome inhibitor ALLN. Actin expression was used as a control. (B) Northern blot of FUS expression in calphostin C-treated (1.5 to 8 h) BCR-ABL-expressing 32Dcl3 cells. (C) In vitro kinase assay (top panel) with recombinant PKCβII as the active kinase and GST-FUS fusion proteins as the substrate. The N-terminal (amino acids 1 to 240) (lane 5) and the C-terminal (amino acids 240 to 526) (lane 6) regions of FUS and four different FUS peptides (lanes 1 to 4) containing the putative PKC phosphorylation sites fused to GST are visible after Coomassie staining of the SDS-PAGE-fractionated kinase reaction products (bottom panel). Data are representative of three different experiments with similar results.