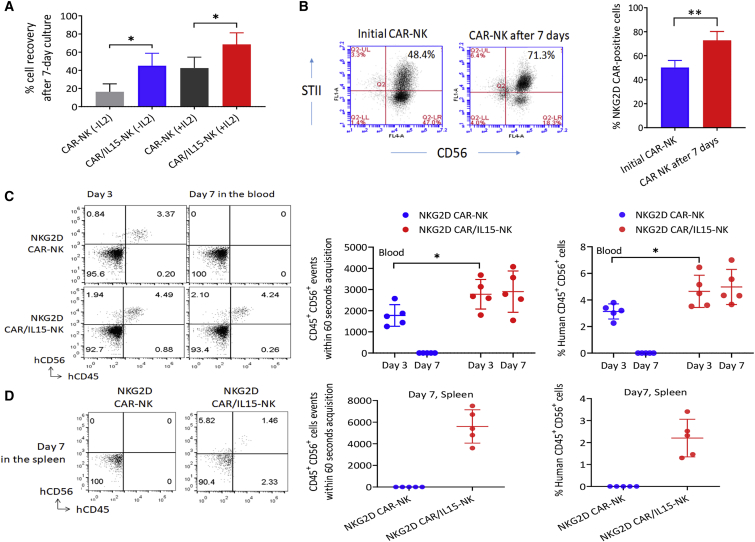
Figure 5.
Effects of ectopically expressed IL-15 on CAR-NK cell persistence
(A) CAR-NK cell recovery after 7-day culture with or without a low concentration IL-2 (10 IU/mL). Cell recovery was calculated as the ratio (%) of the number of cells left to the number of cells initially seeded. The data shown are mean ± SD from four different donors. ∗p < 0.05. (B) Change in the percentage of CAR-NK cells over the 7-day culture without IL-2 (mean ± SD, n = 4). Left: Representative flow charts from one donor. Right: Bar graphs to show the mean percentages of NK cells expressing NKG2D CAR. The data shown are mean ± SD from four different donors. ∗∗p < 0.01. (C) Persistence of human NK cells in mouse peripheral blood. NKG2D CAR-NK cells or NKG2D CAR/IL15-NK cells were i.v. injected into NSG mice (n = 5 per group) through the tail vein and mouse blood samples were collected 3 and 7 days later for flow cytometric analysis. Left: Representative flow charts from one donor. Right: Dot plot with mean point and error bars. The same results are shown in two different ways: (A) CD45 + CD56 + events within 60-s acquisition; and (B) % Human CD45 + CD56 + cells. ∗p < 0.05. The difference between the two types of CAR-NK cells were statistically significant at day 7 (p < 0.001). (D) Mouse spleens were also collected after euthanization of all mice on day 7 for analysis. Left: Representative flow charts from one donor. Right: Dot plot with mean point and error bars. The same results are shown in two different ways. The difference between the two types of CAR-NK cells was statistically significant at day 7 (p < 0.001).