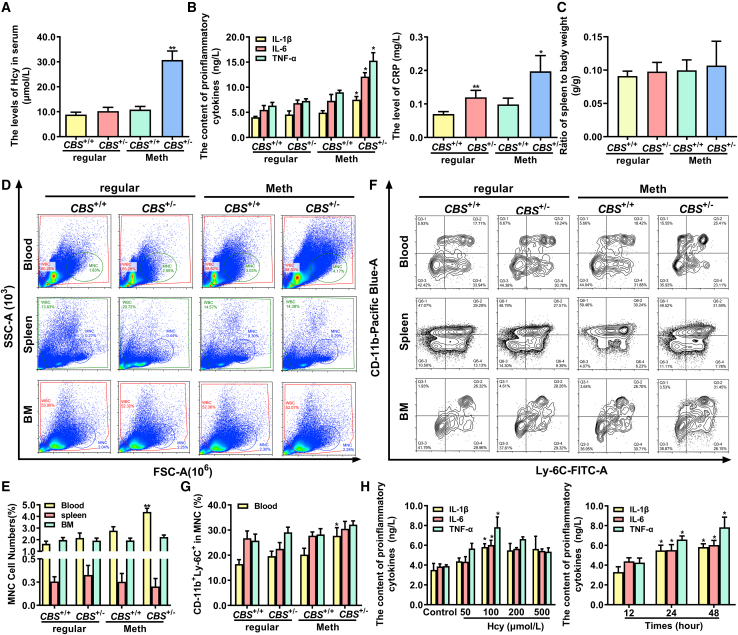
Figure 1.
Hcy enhances inflammation of monocyte-derived macrophages
(A and B) The serum levels of Hcy, proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and CRP in CBS+/+ and CBS+/− mice fed with a regular or methionine diet for 12 weeks. (C) Relative spleen weight to body weight (g/g) in CBS+/+ and CBS+/− mice. (D and E) Monocytes population in peripheral blood, spleen, and bone marrow (BM) from CBS+/+ and CBS+/− mice were analyzed by flow cytometry. SSC, side scattered light; FSC, forward-scatter light. (F and G) The percentages of CD11b+ Ly-6C+ inflammatory monocytes in peripheral blood, spleen, and BM isolated from CBS+/+ and CBS+/− mice were analyzed by flow cytometry. (H) The concentration of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in the supernatants of monocyte-derived macrophages were assayed by ELISA after treatment with different doses of Hcy (0, 50, 100, 200, and 500 μmol/L) for different times (12, 24, and 48 h). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, compared with CBS+/+ or control group.