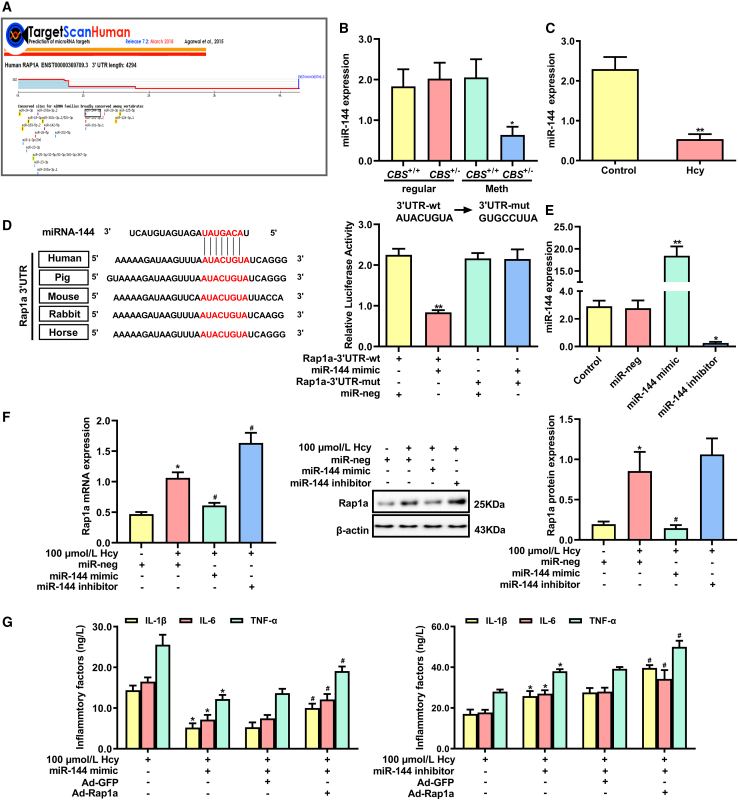
Figure 5.
miR-144 regulates macrophage inflammation induced by Hcy via targeting Rap1a
(A) Prediction of miRNAs that have the potential to target Rap1a by TargetScan database (http://www.targetscan.org/vert_72/). (B) miR-144 expression was detected by qRT-PCR in peripheral monocytes of CBS+/+ and CBS+/− mice. (C) miR-144 expression was detected by qRT-PCR in macrophages treated with 100 μmol/L Hcy for 24 h. (D) Schematic diagram of miR-144 binding site of Rap1a in various species (left panel). Relative luciferase activities in HEK293T cells co-transfected with plasmids of Rap1a-3′ UTR-WT or Rap1a-3′ UTR-mut and miR-144 mimic (right panel). (E) miR-144 expression was detected by qRT-PCR in macrophages transfected with miR-144 mimics or miR-144 inhibitor. (F) qRT-PCR and western blot analysis of Rap1a expression in macrophages transfected with miR-144 mimic, miR-144 inhibitor, and miR-neg. (G) The contents of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in macrophages after co-transduction with Ad-Rap1a and miR-144 inhibitor or miR-144 mimic. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 compared with CBS+/+ + Meth, control, Rap1a-3′ UTR-WT + miR-neg, miR-neg or 100 μmol/L Hcy group, #p < 0.05 compared with 100 μmol/L Hcy + miR-neg, 100 μmol/L Hcy + miR-144 mimic + Ad-GFP group, or 100 μmol/L Hcy + miR-144 inhibitor + Ad-GFP group.