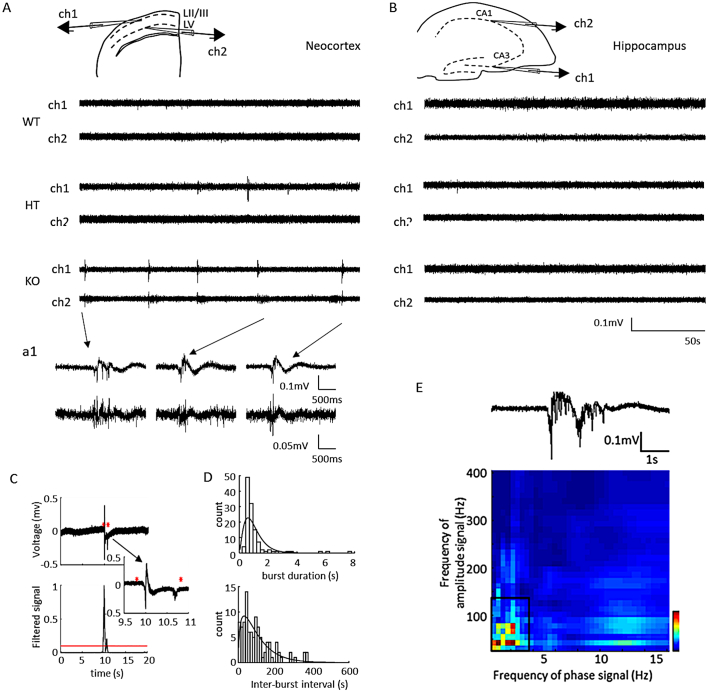
Fig. 1.
In vitro spontaneous bursting activity in the neocortex of Wwox knockout mice. A, Illustration of the placement of field potential recording electrodes in the superficial cortical layer (ch1) and the deep cortical layer (ch2). Field potentials recorded from superficial and deep cortical layers of Cre + wildtype (S-WT), Cre + heterozygote (S-HT) and Cre + knockout (S-KO) littermate mice. a1, Expanded traces of bursting activity present in ch1 and ch2 of the S-KO. Time of bursts indicated by the arrows. B, Illustration of the placement of field potential recording electrodes in the pyramidal cell layer of hippocampal CA3 (ch1) and CA1 (ch2). Field potentials recorded from hippocampal CA1 and CA3 of S-WT, S-HT and S-KO littermates as indicated in A. C, Method used to detect bursting events in the superficial neocortical layer. Stars indicate detected timing of onset and termination of the events. Filtered signal is a convolution of the 4-6 Hz signal with a normalized gaussian (see Methods section for details), highlighting the threshold for event detection. Inset shows expanded trace at times indicated on the horizontal axis. D, Histograms of burst duration and inter-burst interval. The gamma fit distribution of the burst duration has a shape parameter of 2.45 [1.93 3.11] (denoted as: mean [confidence interval of the mean]) for n = 119 bursts, 18 slices, 9 animals. The gamma fit distribution of the inter-burst interval has a shape parameter of 1.43 [1.11 1.84] for n = 101 inter-burst intervals, 18 slices, 9 animals. Median burst duration, inter-burst interval (converted into frequency (bursts/min) are presented in Supplementary Table S1. E, PAC for a burst showing coupling between delta and gamma frequencies. The peak coupling range is indicated by the black boxes. For summary of peak coupling ranges for all bursts, see Supplementary Table S1.