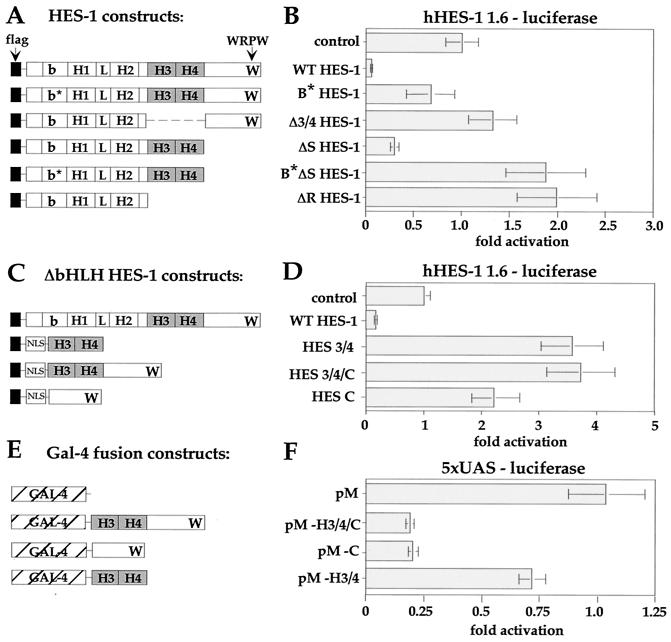
FIG. 8.
Transcriptional analysis of HES-1. The hHES-1 promoter was incorporated upstream of a luciferase reporter gene (hHES-luc) in order to analyze the regulation of the hHES-1 gene by HES-1 in PC12 cells. The luciferase activity of the reporter was corrected for the level of β-Gal activity from a cotransfected internal control plasmid and expressed as fold activity, with the control value normalized as 1.0. (A and B) The function of the H-3/4 domain in HES-1-mediated repression. WT HES-1 strongly repressed transcription from the hHES-1 promoter compared to the control transfected with empty expression vector. In comparison, loss of DNA binding due to mutation of the basic region (B∗ HES-1) resulted in essentially no transcription repression. Furthermore, removal of the H-3/4 domain in Δ 3/4 HES-1 also resulted in a loss of repression activity of the protein, despite the presence of the WRPW motif in the DNA-binding-competent protein. Indeed, HES-1 with the H-3/4 domain (ΔS HES-1), but not the rest of the C terminus (including WRPW), was functional as a modest repressor. The repression activity of this protein was also impaired by the inability to bind to DNA (ΔB∗S HES-1), and instead functioned as a weak activator, or derepressor, of the promoter. Similarly, ΔR HES-1, which lacks both the H-3/4 and the WRPW structures, was also a modest functional activator. (C and D) The role of DNA binding in HES-1-mediated repression. Comparison of the transcription activity of ΔbHLH HES-1 constructs to WT HES-1. Expression of the H-3/4 domain alone (HES 3/4), as well as the WRPW-containing constructs (HES 3/4/C and HES C) with a nuclear-localization signal increased the activity of the promoter. (E and F) Repression function of H-3/4 and WRPW heterologous fusion proteins. The ΔbHLH HES-1 constructs were fused to a heterologous Gal-4 DNA-binding protein (E) and tested for their ability to repress a Gal-4-binding-site-containing reporter construct (with five UAS and a simian virus 40 minimal promoter) (F). The WRPW-containing domains of HES-1 (pM-h3/4/C and pM-C) acted as transcription repressors when fused to Gal-4, consistent with the recruitment to DNA of the corepressor, TLE.