Figure 3.
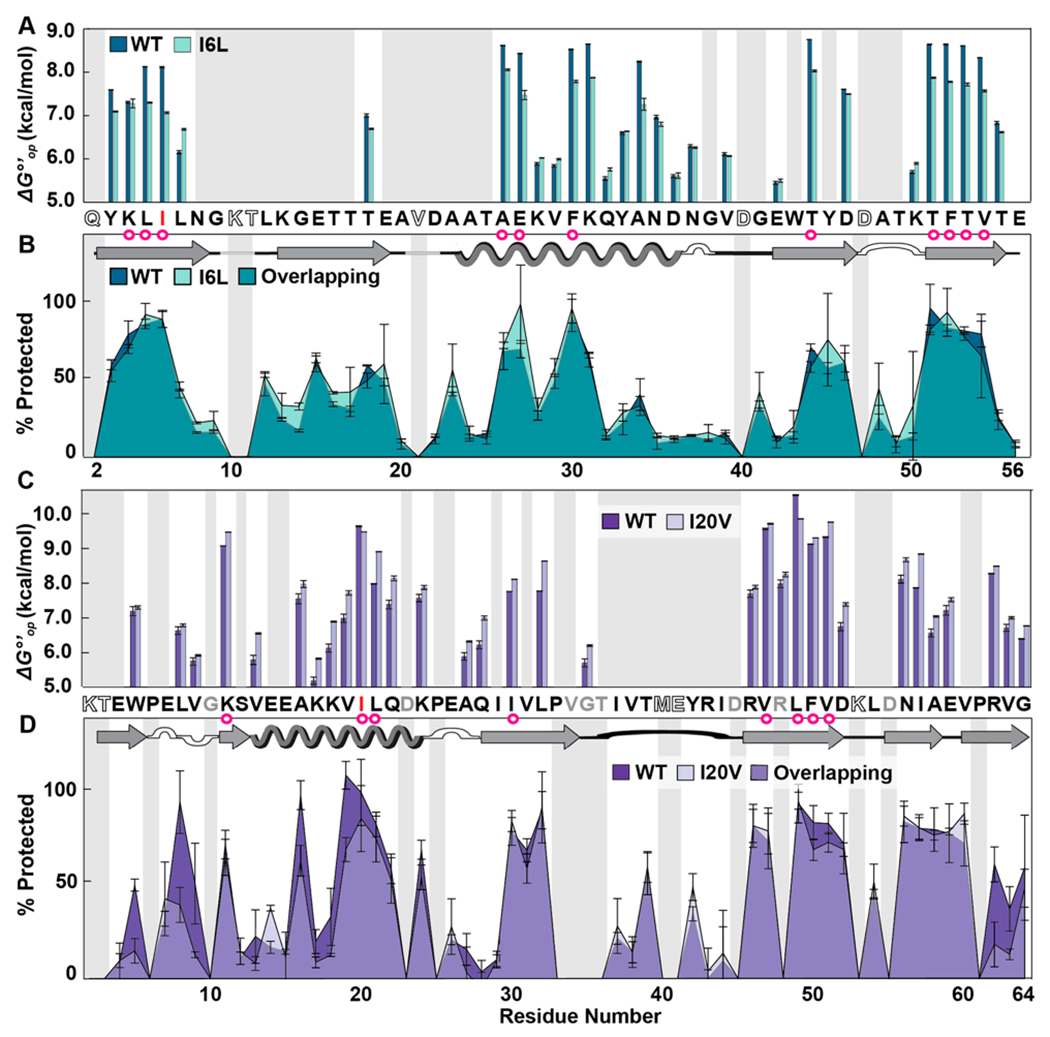
Residue-level solution stabilities and dry state structures of wild-type (WT) and variant proteins. (A) Opening free energies (7.5 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 22 °C). (B) Overlaid LOVE profiles of WT and I6L GB1 freeze-dried in 1.5 mM HEPES pH 6.5. (C) Opening free energies CI2. (D) Overlaid LOVE profiles of WT and I20V CI2 freeze-dried in 1.5 mM HEPES pH 6.5. Primary and secondary structures of the WT proteins are shown between panels. In both primary structures, red letters indicate which residue was mutated. Magenta circles indicate solution global-unfolding residues of WT proteins. Gray boxes indicate data that are missing due to rapid back exchange (open letters in primary structure) and/or the inability to reliably integrate peak volumes due to overlapping resonances (gray letters in primary structure). Error bars represent standard deviations from the mean calculated from triplicate analysis.
