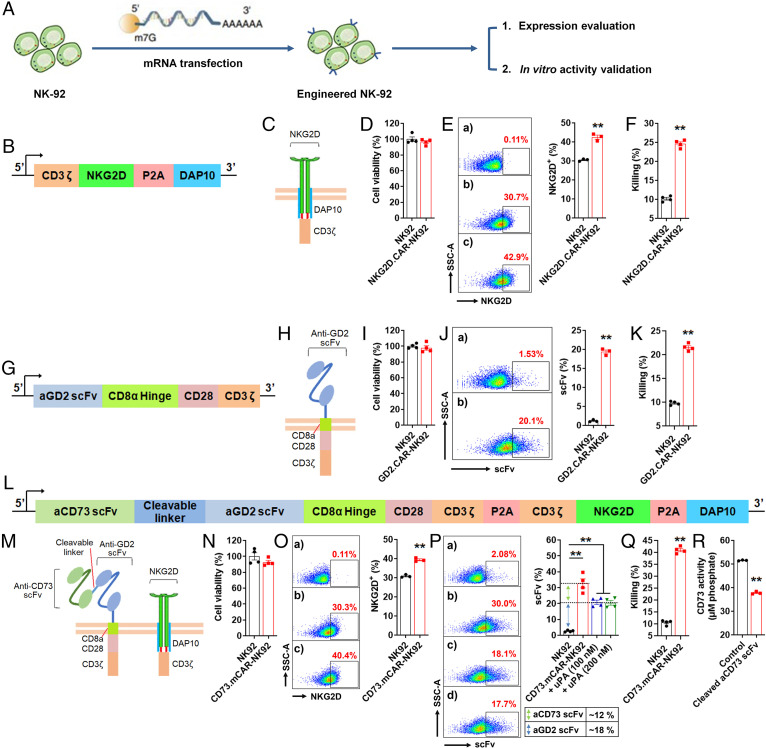
Fig. 2.
Functional validation of genetic construct components. (A) A schematic illustration showing the process of engineering NK-92 cells and evaluation of their activity. (B) Transgene structure encoding NKG2D.DAP10.CD3ζ-CAR. (C) Schematic illustration of NKG2D.DAP10.CD3ζ-CAR structure. (D) Cell viability (%) of NK-92 cells after 48 h transfection with NKGD2.CAR gene (n = 4). (E, Left) NKG2D expression on NKG2D.CAR-NK92 cells (n = 3). a-b represent NK-92 cells stained with isotype and APC-anti-NKG2D antibodies. c represents NKG2D.CAR-NK92 cells stained with APC-anti-NKG2D antibody. (Right) NKG2D expression (%) on control NK-92 and NKG2D.CAR-NK92 cells. (F) In vitro cytotoxicity of NKG2D.CAR-NK92 and control NK-92 cells against GBM43 cells at an E/T ratio of 5 over 8 h (n = 4). (G) Transgene structure encoding GD2.CD28.CD3ζ-CAR. (H) Schematic illustration of GD2.CD28.CD3ζ-CAR structure. (I) Cell viability (%) of NK-92 cells after 48 h transfection with GD2.CAR gene (n = 4). (J, Left) Anti-GD2 scFv expression determined by flow cytometry on GD2.CAR-NK92 cells (n = 3). a represents NK-92 cells stained with Biotin-protein L + APC-streptavidin antibodies. b represents GD2.CAR-NK92 cells stained with Biotin-protein L + APC-streptavidin antibodies. (Right) GD2.CAR expression (%), on control NK-92 cells and GD2.CAR-NK92 cells. (K) In vitro cytotoxicity of GD2.CAR-NK92 and control NK-92 cells against GBM43 cells at an E/T ratio of 5 over 8 h (n = 4). (L) Transgene structure of the full multifunctional construct: tumor-responsive anti-CD73 scFv-secreting dual-specific CAR targeting NKG2DL and GD2. (M) Schematic illustration of the full construct. (N) The cell viability (%) of NK-92 cells after 48 h transfection with the full construct gene (n = 4). (O) NKG2D expression on CD73.mCAR-NK92 cells. a–b represent NK-92 cells stained with isotype and APC-anti-NKG2D antibodies; c represents CD73.mCAR-NK92 cells stained with APC-anti-NKG2D. (P, Left) Expression of anti-CD73 scFv and anti-GD2 scFv on CD73.mCAR-NK92 cells determined by flow cytometry. a represents NK-92 cells stained with Biotin-protein L + APC-streptavidin; b–d represent non-treated, 100 nM uPA-treated, and 200 nM uPA-treated CD73.mCAR-NK92 cells stained with Biotin-protein L + APC-streptavidin, respectively. (Right) Calculation of the anti-CD73 scFv and anti-GD2 scFv expression (%) on CD73.mCAR-NK92 cells. (Q) In vitro cytotoxicity of NK-92 and CD73.mCAR-NK92 cells against GBM43 cells at an E/T ratio of 5 over 8 h (n = 4). (R) Enzymatic activity of CD73 on GBM43 cells after incubation with cleaved aCD73 scFv following release from uPA-treated CD73.mCAR-NK92 cells (n = 3). Data represent independent samples. Data are shown as mean ± SEM, **P < 0.01. P values in E, F, J, K, O, Q, and R were determined using the two-tailed Student’s t test and in P using one-way ANOVA analysis.