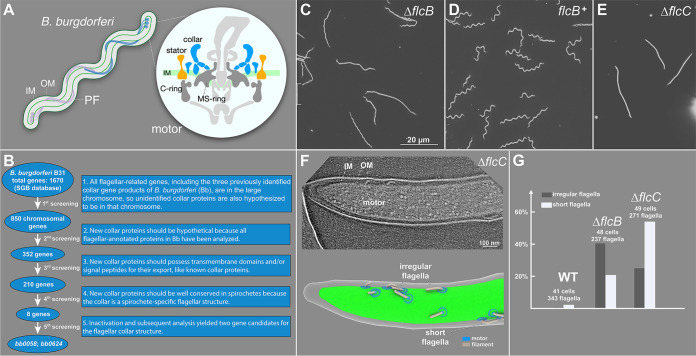
FIG 1.
BB0058 (FlcB) and BB0624 (FlcC) are potential collar proteins in B. burgdorferi. (A) Schematic models of the periplasmic flagellum (PF) and motor in a B. burgdorferi cell. IM, inner membrane; OM, outer membrane. (B) Based on the common features of the previously identified flagellar collar proteins, all 1,670 gene-encoded proteins of B. burgdorferi were manually screened from the Spirochetes Genome Browser (http://sgb.leibniz-fli.de/cgi/list.pl?sid=24&c_sid=yes&ssi=free). Transmembrane domains and signal peptides were predicted using TMHMM, Phobius, and SignalP 5.0 programs. Subsequent screenings resulted in identification of eight potential candidate collar proteins. (C to E) Dark-field microscopic images showing the characteristic rod-shaped morphology of ΔflcB mutant cells, flat-wave morphology of complemented flcB+ cells, and rod-shaped morphology of ΔflcC mutant cells, respectively. (F) A representative tomographic slice of the ΔflcC cell tip (top) and corresponding 3D surface view (bottom), showing the irregular and short flagella in the mutant cell. (G) Statistical analysis of the flagellar phenotype in WT, ΔflcB, and ΔflcC cells. A normal flagellum is defined as being oriented toward the other pole of the cell body. An abnormal or irregular periplasmic flagellum is defined as being tilted toward the cell pole from where it originated. The total number of cells and periplasmic flagella analyzed for each strain is shown at the top of the corresponding column.