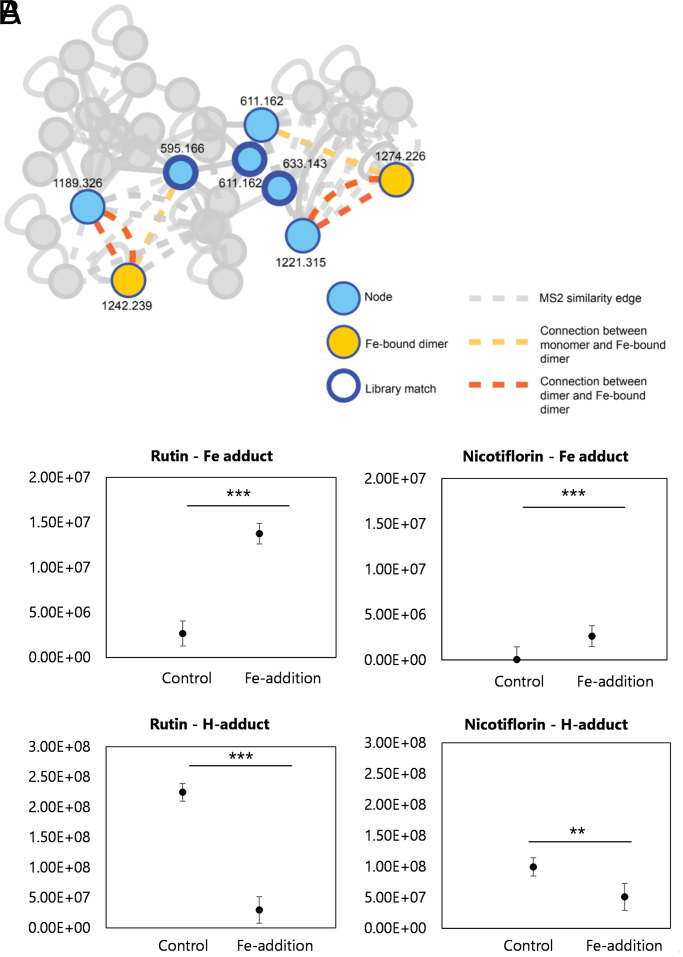
Fig. 6.
Native spray metal metabolomics network identifies iron-binding activity of rutin and nicotiflorin. (A) Post-LC infusion of Fe3+ or H+ with subsequent MS/MS-based GNPS analysis highlights rutin and nicotiflorin were the only compounds in the full network to complex with iron based on ion identity molecular networking. Edges are based on MS/MS similarity (gray in the absence of binding iron). Both pure compounds (rutin, m/z 611.162; nicotiflorin, m/z 595.166) were detected to bind iron as dimers with strong connections to monomeric (yellow edges) and dimeric (orange edges) molecular ions of each compound alone, with these peaks absent in control experiments without iron supplementation. Nodes corresponding to binding of an H+ ion (blue) are shown with a thick outline representing a library match to MoNA MS/MS library in GNPS. (B) Integrated peak intensities of dimer peak (2M + H adduct) and iron-bound dimer peak (2M + Fe – 2H adduct) in the control (no infusion) and Fe-infusion samples. Shown are the results from three replicates with the average indicated with a horizontal line. Statistical significance between integrated peak areas was calculated using a Student’s t test (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01).