Figure 1.
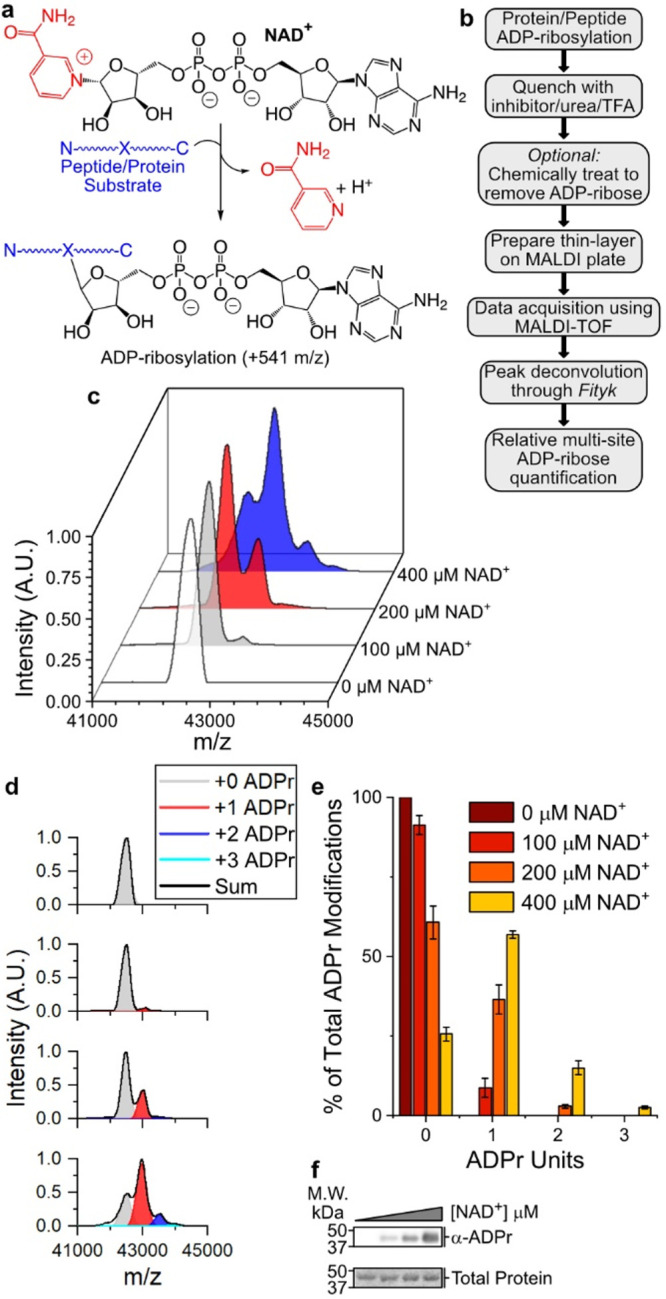
P14 auto-ADP-ribosylates at a single site under physiological conditions. (a) ADP-ribosylation reaction catalyzed by PARP enzymes. (b) TLC-MALDI workflow. (c) P14 was incubated in the presence of increasing concentrations of NAD+ and was subjected to TLC-MALDI to visualize the resulting increase in m/z due to ADPr (+541). (d) MS spectra were integrated to determine the relative levels of auto-ADP-ribosylation. (e) Quantification of the results in (b). The bar graphs depict the fraction of the total P14 protein that has been modified at 0, 1, or 2 distinct sites (mean ± S.E.M., n = 3). (f) In vitro P14 ADP-ribosylation assay.
