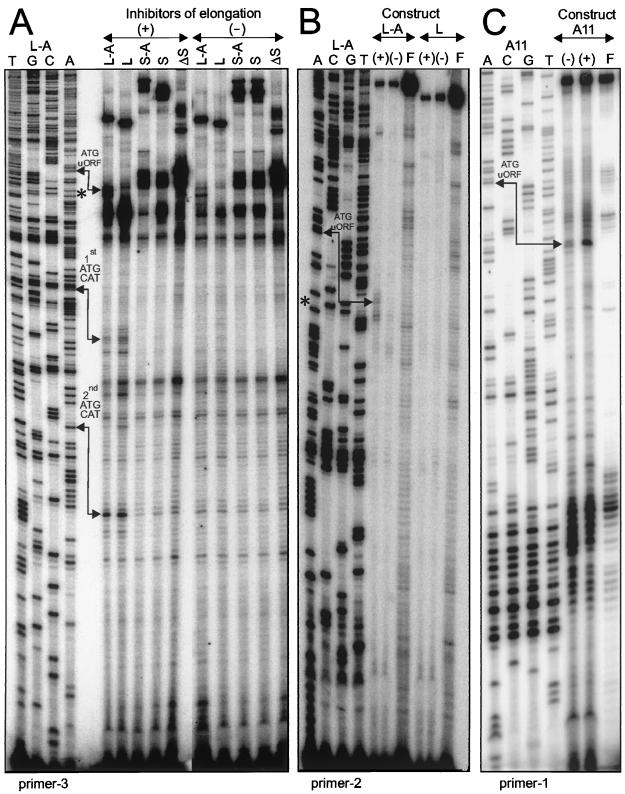
FIG. 3.
Toeprinting of translation initiation complexes. Translation initiation reactions were performed in the presence (+) or absence (−) of translation elongation inhibitors on transcripts with linear (L-series) or structured (S-series and A11) leaders, as depicted in Fig. 1A and 4 (A11). Reverse transcription reactions performed with antisense primer 3, 2, or 1 resulted in extended cDNA products analyzed by PAGE (6% gel). Formation of a functional 80S ribosome complex at the initiation ATG codon resulted in premature reverse transcription termination 17 to 18 nt downstream from the A base. Toeprints corresponding to translation initiation complexes located at the first and the second, out-of-frame ATG codons of CAT were detected with primer 3 on both linear transcripts (A). Note that primer 2 did not detect any toeprint band at the ATG of CAT on L and L-A mRNAs, as its target site partially overlaps the region protected by the initiating ribosome. An initiation complex at uORF A was detected with both primer 3 and primer 2 on transcript L-A (A and B) and with primer 1 on transcript A11 (C). Lanes F in panels B and C contain products of the control translation initiation reactions performed in the absence of the wheat germ extracts; lanes A, C, G, and T contain products of the sequencing reactions performed on the corresponding plasmids, as indicated. Positions of the hairpin are shown within the L-A sequence (A and B) by asterisks corresponding to cytosine 122 (Fig. 1A).