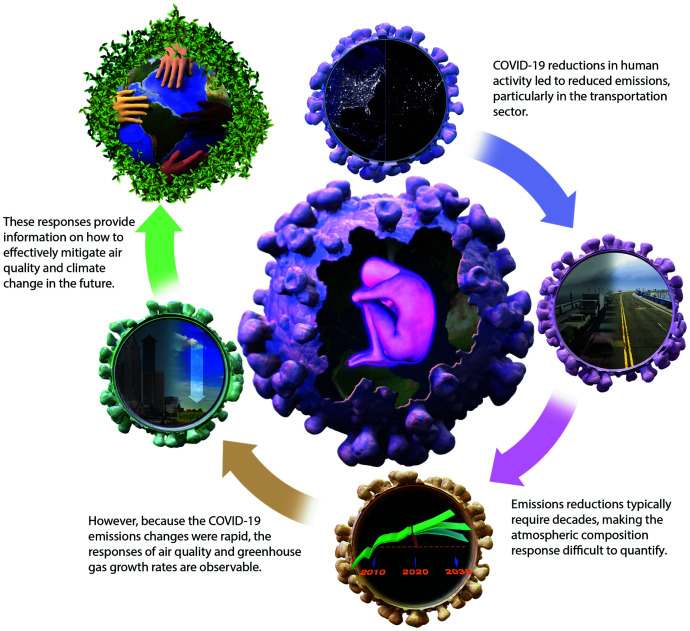
Fig. 1.
Illustration of the conceptual foundation for this study. The COVID-19–induced reductions in human activity led to reduced anthropogenic emissions. The fact that these reductions occurred over months rather than decades allows us to observe how the atmosphere, land, and ocean are likely to respond in a future scenario with stricter emissions controls. This analysis helps to identify effective pathways to mitigate air pollution and climate-relevant GHG emissions. Image credit: Chuck Carter (Keck Institute for Space Studies, Pasadena, CA).